Dyshidrotic eczema, also known as pompholyx or dyshidrosis, is a type of eczema that affects the hands and feet. Characterized by small, itchy blisters, dyshidrotic eczema can be a chronic and recurring condition that significantly impacts a person’s quality of life. This article provides a comprehensive overview of dyshidrotic eczema, including its symptoms, causes, treatment options, and preventive measures.
What Is Dyshidrotic Eczema?
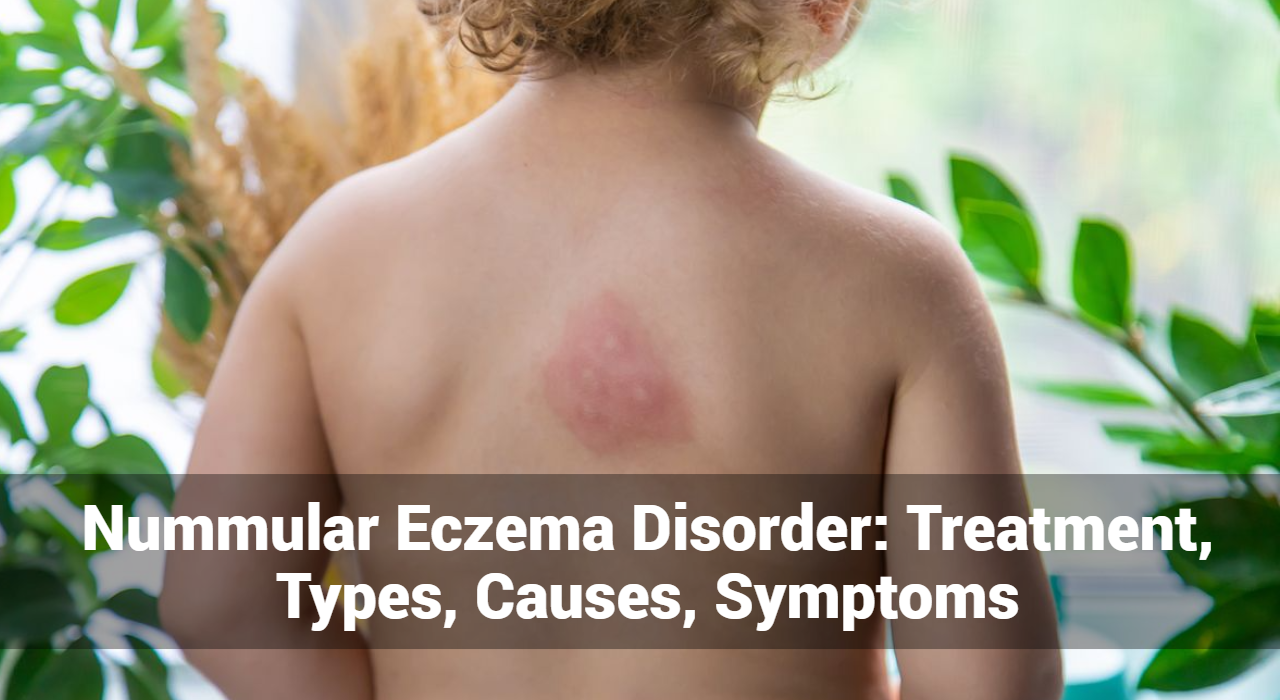
Dyshidrotic eczema is a skin condition that primarily affects the palms of the hands, sides of the fingers, and soles of the feet. The condition manifests as small, fluid-filled blisters that cause intense itching and discomfort. These blisters can persist for several weeks, causing significant pain and potentially leading to skin cracking and infection.
Epidemiology
Dyshidrotic eczema is relatively common, affecting approximately 1 in 5,000 people. It can occur at any age but is most frequently seen in adults aged 20 to 40. The condition tends to be more prevalent in warmer climates and during spring and summer months.
What Are The Different Types of Dyshidrotic Eczema?
Dyshidrotic eczema, also known as pompholyx, is a specific type of eczema that affects the hands and feet. While it is generally considered a single condition, dyshidrotic eczema can present in various forms, which can be classified based on severity, chronicity, and underlying triggers. Here, we’ll explore these variations in detail.
1. Acute Dyshidrotic Eczema
Characteristics:
- Sudden onset of symptoms.
- Development of small, intensely itchy blisters on the palms, sides of the fingers, and soles of the feet.
- The blisters are often filled with a clear fluid and can cause significant discomfort.
Causes:
- Acute flare-ups may be triggered by stress, allergens, or exposure to irritants.
- Changes in weather or humidity levels can also provoke an acute episode.
Symptoms:
- Intense itching and burning sensation.
- Redness and swelling around the blistered areas.
Treatment:
- Topical corticosteroids to reduce inflammation.
- Cold compresses to alleviate itching.
- Avoiding known triggers to prevent future flare-ups.
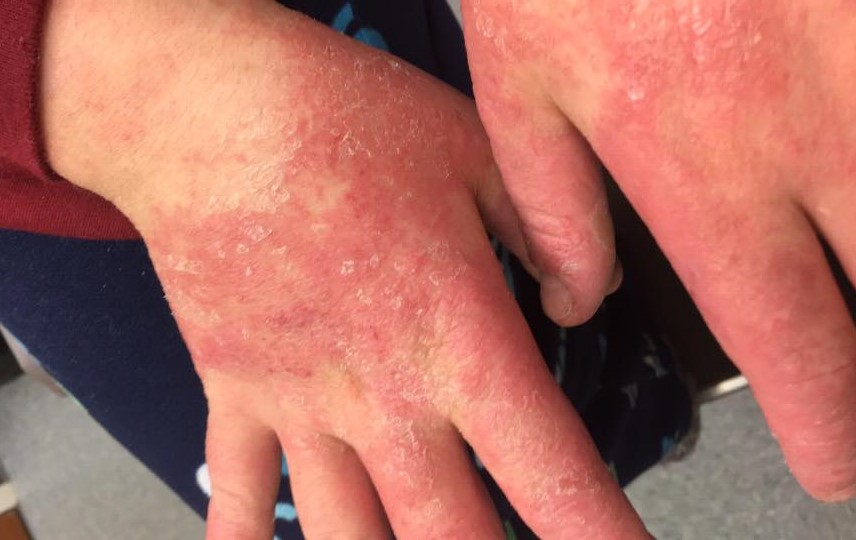
2. Chronic Dyshidrotic Eczema
Characteristics:
- Persistent or recurring episodes over a long period.
- Skin thickening (lichenification) and fissures due to chronic scratching and inflammation.
Causes:
- Ongoing exposure to irritants or allergens.
- Underlying medical conditions like atopic dermatitis.
Symptoms:
- Continuous or frequently recurring blisters.
- Dry, cracked, and thickened skin.
Treatment:
- Long-term use of emollients to maintain skin hydration.
- Topical or oral corticosteroids during flare-ups.
- Lifestyle modifications to minimize exposure to triggers.
Track and Manage your Eczema treatment using a comprehensive Eczema App
Download Eczemaless now
3. Recurrent Dyshidrotic Eczema
Characteristics:
- Episodes that occur in cycles, with periods of remission in between.
- Blisters reappear periodically, often without an apparent trigger.
Causes:
- Allergens, stress, or other environmental factors that periodically affect the patient.
Symptoms:
- Similar to acute dyshidrotic eczema but with intermittent flare-ups.
- Clear fluid-filled blisters, itching, and redness.
Treatment:
- Preventive measures during remission phases, such as maintaining a consistent skincare routine.
- Quick intervention with topical treatments at the onset of symptoms.
4. Hyperkeratotic Dyshidrotic Eczema
Characteristics:
- Development of thick, scaly patches on the hands and feet.
- Often accompanied by fewer blisters compared to other forms.
Causes:
- Chronic irritation and inflammation.
- Genetic predisposition to hyperkeratosis.
Symptoms:
- Thickened, scaly skin that can crack and bleed.
- Mild to moderate itching.
Treatment:
- Keratolytic agents like salicylic acid to reduce skin thickening.
- Emollients to soften the skin.
- Topical steroids for inflammation.
5. Vesicular Dyshidrotic Eczema
Characteristics:
- Presence of numerous small vesicles (blisters) filled with clear fluid.
- Blisters are more numerous and can merge to form larger bullae.
Causes:
- Similar triggers as other forms, including allergens, stress, and irritants.
Symptoms:
- Intense itching and burning sensation.
- Blisters that may rupture, leading to crusting and potential secondary infection.
Treatment:
- Antihistamines to control itching.
- Antiseptic soaks to prevent infection.
- Topical steroids for severe inflammation.
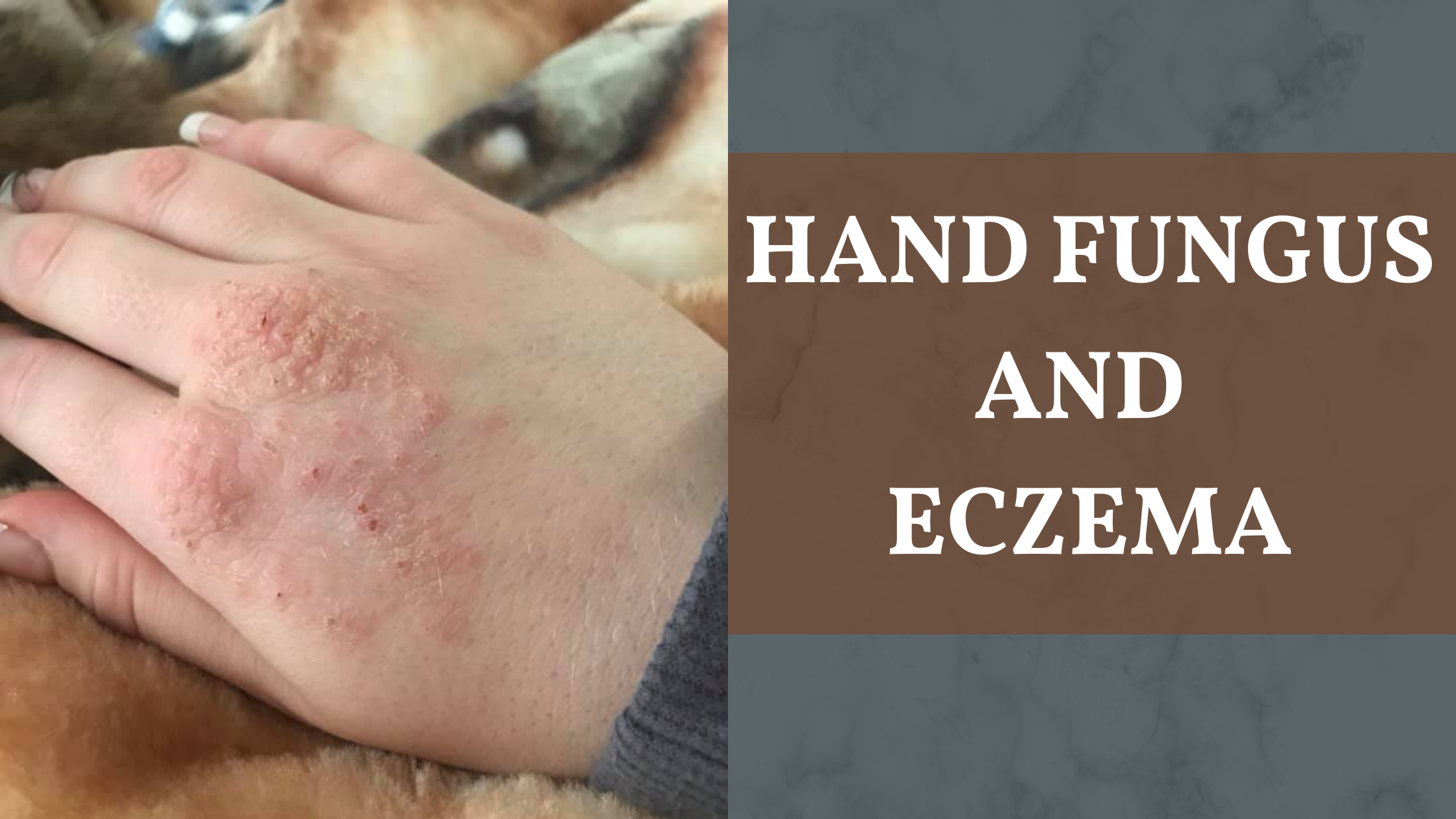
6. Infective Dyshidrotic Eczema
Characteristics:
- Secondary bacterial or fungal infection superimposed on dyshidrotic eczema.
- Increased severity and risk of complications.
Causes:
- Open blisters and cracked skin can become infected with bacteria (e.g., Staphylococcus aureus) or fungi (e.g., Candida species).
Symptoms:
- Increased redness, swelling, and pain.
- Pus formation and potential fever.
Treatment:
- Antibiotics or antifungal medications to treat the infection.
- Continued use of moisturizers and topical steroids once the infection is controlled.
7. Allergic Dyshidrotic Eczema
Characteristics:
- Triggered by an allergic reaction to substances such as metals (nickel), certain foods, or topical products.
- Blisters appear after contact with or ingestion of the allergen.
Causes:
- Allergic contact dermatitis can provoke dyshidrotic eczema in susceptible individuals.
Symptoms:
- Blistering, itching, and redness localized to areas in contact with the allergen.
- Systemic symptoms if caused by ingested allergens.
Treatment:
- Identification and avoidance of the allergen.
- Topical steroids to reduce allergic inflammation.
- Antihistamines to control itching.
Symptoms of Dyshidrotic Eczema
Primary Symptoms
- Blisters: Small, fluid-filled blisters that typically appear on the fingers, palms, and soles. These blisters can be extremely itchy and painful.
- Itching: Intense itching is a hallmark of dyshidrotic eczema, often preceding the appearance of blisters.
- Redness: The affected areas may become red and inflamed.
- Cracking and Peeling: As blisters heal, the skin may crack, peel, and become painful.
Secondary Symptoms
- Pain: Severe itching and blistering can lead to significant pain, especially if the skin cracks or becomes infected.
- Swelling: Affected areas may swell due to inflammation and fluid buildup.
- Dryness: Skin may become dry and scaly after blisters resolve.
- Infection: Open blisters and cracked skin can become infected, leading to increased pain, pus formation, and other complications.
Complications
- Skin Infections: Bacterial infections can develop if blisters or cracked skin are not properly managed.
- Scarring: Repeated episodes and chronic inflammation can lead to permanent skin changes and scarring.
- Psychosocial Impact: Persistent symptoms can affect mental health, causing stress, anxiety, and social embarrassment.
GET IN CONTROL OF YOUR ECZEMA
Use our AI tool to check the severity of Eczema and keep track of your Eczema progress.
What Are The Causes of Dyshidrotic Eczema?
Genetic Factors
- Family History: A family history of eczema or other atopic conditions can increase the risk of developing dyshidrotic eczema.
- Genetic Mutations: Certain genetic mutations, particularly those affecting skin barrier function, may predispose individuals to this condition.
Environmental Factors
- Allergens: Exposure to allergens such as pollen, dust mites, and pet dander can trigger dyshidrotic eczema in susceptible individuals.
- Irritants: Contact with irritants like soaps, detergents, and chemicals can exacerbate symptoms.
- Climate: Warm, humid climates and seasonal changes can influence the severity and frequency of outbreaks.
Lifestyle Factors
- Stress: Psychological stress is a known trigger for dyshidrotic eczema flare-ups.
- Diet: Certain foods, such as those high in nickel or cobalt, may trigger symptoms in some individuals.
- Hygiene Practices: Excessive washing and use of harsh skin products can damage the skin barrier and exacerbate symptoms.
Medical Conditions
- Atopic Dermatitis: Individuals with a history of atopic dermatitis are more likely to develop dyshidrotic eczema.
- Allergies: Allergic conditions, including hay fever and asthma, are often associated with dyshidrotic eczema.
- Infections: Fungal infections on the feet or hands can trigger dyshidrotic eczema in some cases.
Diagnosis of Dyshidrotic Eczema
Clinical Evaluation
- Medical History: A detailed medical history, including any family history of eczema or allergies, helps in diagnosing dyshidrotic eczema.
- Physical Examination: A dermatologist will examine the skin, noting the characteristic blisters and pattern of distribution.
Diagnostic Tests
- Skin Biopsy: A biopsy may be performed to rule out other conditions that mimic dyshidrotic eczema, such as contact dermatitis or fungal infections.
- Patch Testing: Patch testing can identify specific allergens that may be triggering the eczema.
- Blood Tests: Blood tests may be used to check for underlying conditions or infections that could be contributing to symptoms.
Treatment of Dyshidrotic Eczema
Topical Treatments
- Corticosteroids: Topical corticosteroids are commonly prescribed to reduce inflammation and itching. They are applied directly to the affected areas.
- Calcineurin Inhibitors: Non-steroidal options such as tacrolimus and pimecrolimus can help manage symptoms with fewer side effects than steroids.
- Moisturizers: Emollients and moisturizers are essential for maintaining skin hydration and barrier function.
Oral Medications
- Antihistamines: Oral antihistamines can help reduce itching and improve sleep.
- Corticosteroids: For severe cases, oral corticosteroids may be prescribed to quickly control inflammation.
- Immunosuppressants: Medications like cyclosporine or methotrexate may be used in severe, refractory cases.
Phototherapy
- UV Therapy: Ultraviolet light therapy, particularly narrowband UVB, can be effective in reducing symptoms for some patients.
Lifestyle and Home Remedies of Dyshidrotic Eczema
- Cold Compresses: Applying cold compresses to affected areas can reduce itching and inflammation.
- Avoiding Triggers: Identifying and avoiding triggers, such as certain foods, stress, or allergens, can help manage symptoms.
- Good Hygiene Practices: Using mild soaps and moisturizers, and avoiding excessive washing, can help protect the skin barrier.
Alternative Treatments
- Natural Remedies: Some patients find relief using natural treatments such as coconut oil, aloe vera, or apple cider vinegar.
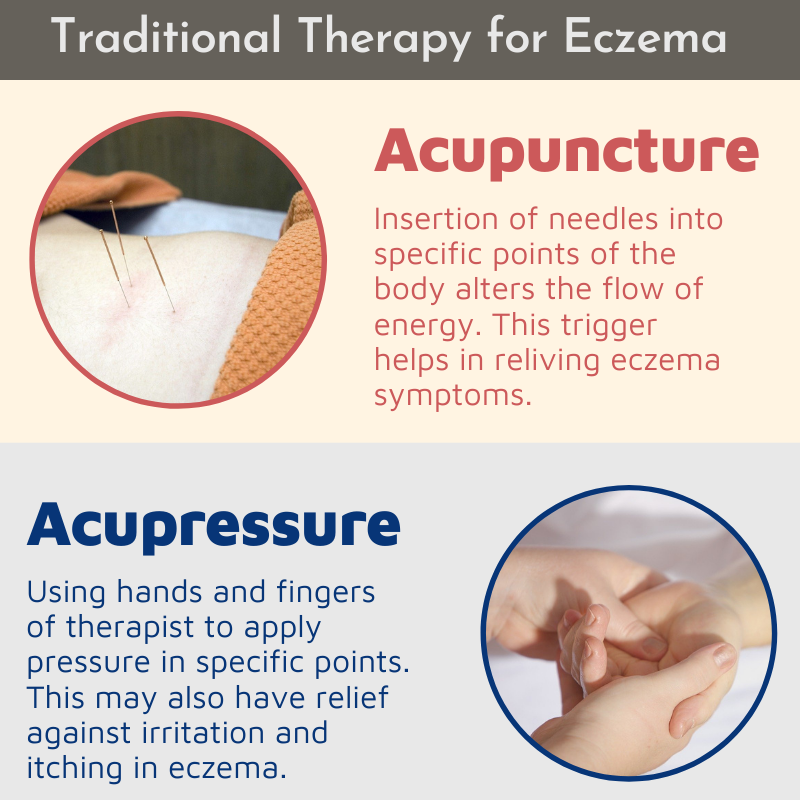
- Acupuncture: Although not widely studied, some individuals report benefits from acupuncture.
Preventive Measures
- Skin Care Routine: Establishing a consistent skin care routine with gentle, hydrating products is crucial.
- Protective Clothing: Wearing gloves when handling irritants and breathable fabrics can help prevent flare-ups.
- Stress Management: Techniques such as yoga, meditation, and counseling can help manage stress levels.
Conclusion
Dyshidrotic eczema is a challenging condition that requires a multifaceted approach to management. Understanding the symptoms, causes, and treatment options can empower patients to take control of their condition and improve their quality of life. By working closely with a dermatologist and implementing preventive measures, individuals with dyshidrotic eczema can achieve better skin health and reduce the impact of this chronic condition on their daily lives.
Track and Manage your Eczema treatment using a comprehensive Eczema App
Download Eczemaless now