Table of contents
- Introduction
- What are topical steroids?
- How topical steroids are prescribed?
- How to apply topical steroids?
- What is a fingertip unit (FTU)?
- Pros and cons of topical steroids
- What are side effects of topical steroids?
- What is topical steroid withdrawal?
- What should you be careful about when using steroids?
- Conclusion
Introduction
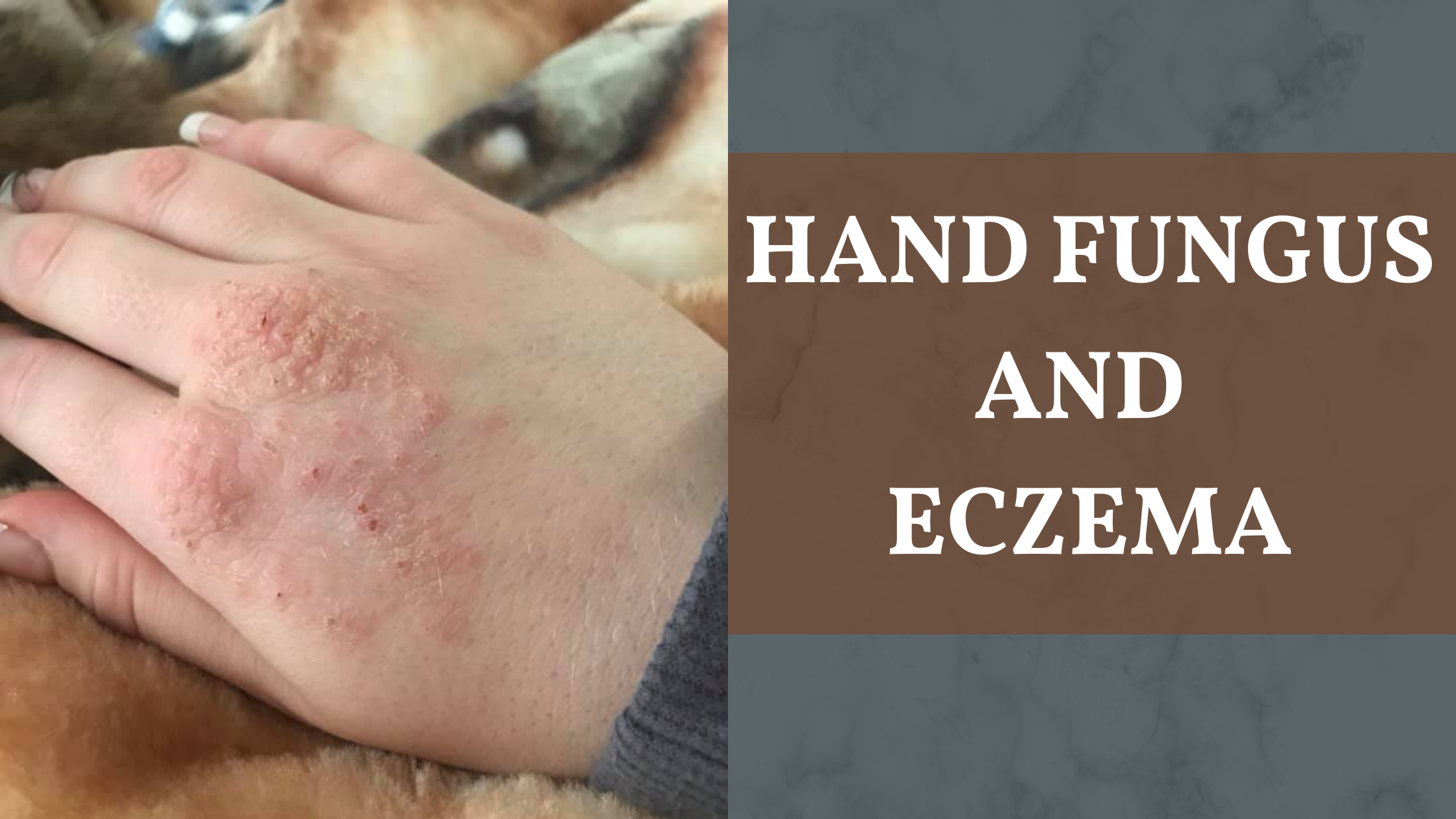
Topical steroids are medicated creams that can be applied on skin to treat eczema. It is a very effective treatment in addition to emollients (moisturizers). A short course of prescription steroid cream for eczema is enough to clear up an eczema flare. If you use it for short periods, side effects are uncommon. Steroids reduce skin inflammation which occurs in eczema.
Eczema or atopic dermatitis is an inflammation of the skin leading to red, itchy rash.
What are topical steroids?
Steroids also known as corticosteroids belong to a group of medications known as glucocorticoids. Topical steroid is an anti-inflammatory preparation. Apart from being anti-inflammatory, it also acts by being immunosuppressive, anti-proliferative and vasoconstrictive. Steroid containing topical products include creams, ointments and lotions. Creams work best in treating moist or weeping areas of eczematous skin. They are usually white. Ointments are best to treat dry and thickened areas of skin. They are usually clear. Lotions are used to treat hairy regions such as scalp. They are thin creams.
Steroids work by reducing the inflammation of your skin. They are used for many skin conditions and eczema is one of them. Prescription steroid cream for eczema is effective in treating eczema.
There are several types of topical steroids and they are categorized according to their strength. Greater the potency or strength, more effective it will be in reducing inflammation but on the other hand side effects will be more with continued use.
- Mild – Ex: 1% Hydrocortisone
- Moderately potent – Ex: Prednicarbate
- Potent (strong) – Ex: Betamethasone valerate, Mometasone furoate
- Very potent – Ex: Clobetasol propionate
How topical steroids are prescribed?
When there is one or more patches of an eczema flare-up, a course of topical steroid is used. Once the flare-up is cleared, the topical steroid treatment can be stopped. The aim is to use the lowest strength of topical steroid to minimize the side effects, but strong enough to clear your flare up.
Ex: 1% Hydrocortisone is used to treat eczema in children
Usually topical steroids must not be used for prolonged periods on large areas of the body. This rule is important especially for children. For severe inflammatory eczema, a very potent topical steroid will be used such as Clobetasol propionate. A small amount should be applied on affected areas while gently massaging into skin.
Sometimes your doctor or the dermatologist will use 2 or more preparations of different strengths at the same time.
Ex:
- Mild topical steroid for eczema lesions on the face
- Moderately potent steroid for lesions on arms and legs where your skin is thicker
- A very potent steroid is needed for eczema on your palms and soles as the skin is thick in these areas.
Usually a short course of topical steroids for 7 -14 days is enough to clear a flare-up although sometimes longer courses are required. Some dermatologists will try a short course of a strong topical steroid usually for 3 days to treat a mild to moderate flare. This method is quick and quite safe. How often a steroid course is necessary will depend on how often you get a flare and it greatly varies from person to person. Once the steroid topical course is over, emollients must be continued daily to prevent further flares of eczema. Therefore, prescription steroid cream for eczema for a short period usually gives relief.
For people with frequent flares of eczema, a steroid can be applied on the usual sites where you get a flare up for 2 days every week. This is known as weekend therapy. It helps to prevent a flare up from occurring.
How to apply topical steroids?
Topical steroids can be applied once or twice a day according to your doctor’s advice. A fingertip unit is the correct dose and it is a small amount that has to be gently rubbed on the areas of inflamed skin until it disappears. Although moisturizers are applied liberally, topical steroids must be applied carefully.
First apply your emollient and wait for 10-15 minutes, before applying the prescription steroid cream for eczema. Wash your hands after application.
Track and Manage your Eczema treatment using a comprehensive Eczema App
Download Eczemaless now
What is a fingertip unit (FTU)?
A fingertip unit is the amount of steroid that is squeezed out from a tube (standard size with a 5mm nozzle) along an adult’s fingertip. 1 FTU is enough to treat an area, twice the size of an adult palm with fingers together.
Pros and cons of topical steroids
Topical steroids are especially useful in treatment of any inflammatory skin condition. It is very effective to treat a flare-up of eczema. However there are certain side effects which you have to know.
What are the side effects of topical steroids?
A short course (less than 4 weeks) of topical steroids is generally safe and side effects are rare. Problems arise when you continue to use topical steroids for prolonged periods or if strong steroids are used frequently. Side effects are common if strong topical steroids are used long term. The side effects can be local or systemic.
Local side effects (affecting the area treated and a bit of surrounding skin)
- Burning or stinging sensation – This is common when you apply a topical steroid for the first time. Once your skin gets used to the treatment, this feeling will subside.
- Skin atrophy (Thinning of skin) – although uncommon with normal regular use, it occurs especially if a potent steroid is used under occlusion (air tight dressing).
- Worsening or triggering other skin conditions like acne, Rosacea and perioral dermatitis.
- Develop striae (permanent stretch marks), telangiectasia (thin spidery blood vessels), easy bruising and discoloration. These are common with long term use of topical steroids.
- Changing of skin color – This is noticeable more in people with dark complexion.
- Growth of hair will increase in the treated area of skin
- Allergic reactions – This may occur usually to the preservatives used in the steroid product. It can irritate your skin and worsen inflammation.
Systemic effects (affecting your whole body)
This is rare with topical steroids but can occur when strong steroids are used for long periods. The steroid can get absorbed in to your blood stream.
- Affecting the growth of children – If children need repeated doses of strong topical steroids, their growth must be monitored.
- Increase of blood pressure
- Increase of blood cholesterol levels
- Fluid retention (Collection of fluid in legs)
- Baldness (thinning of hair in scalp)
- Features of Cushing syndrome – weight gain, skin thinning, mood changes, buffalo hump in the neck, purple color striae, moon face etc.
Although there is a common fear of treatment, the risk of side effects is lower than most of us think, as long as it is applied as prescribed and not used longer than necessary.
What is topical steroid withdrawal?
This can occur when treated with a moderate strength or potent steroid which is stopped suddenly. The symptoms of topical steroid withdrawal include red skin, stinging, burning pain, itching, excessive sweating and peeling of skin. The severity of symptoms may vary from mild short lived to severe long term. The symptoms will gradually settle, sometimes leaving your skin dry and itchy for prolonged periods.
What should you be careful about when using steroids?
- Do not undertreat because you are too cautious – always apply as prescribed to clear your flare up.
- Avoid using too much – you might want to continue topical steroids daily, even after your eczema has cleared, in order to prevent a future flare. You should not use steroids for long periods without close supervision by a doctor. However, you can apply moisturizers liberally every day which will help you to prevent a flare up of eczema.
In order to prevent side effects, the strength or potency of the topical steroid needs to be adjusted to the sensitivity and thickness of the skin area which needs to be treated.
Steroids become more potent in your face, eye lids, genitals, inner sides of joints and arm pits because the skin is thin and sensitive. Therefore, steroids of low or medium potency is enough to treat eczema in these regions. Higher potency steroids are needed for scalp, palms and soles as the skin here is thick and the medication should reach deeper layers of skin.
The effect will be stronger when topical steroids are applied to wet skin. It acts better when applied after taking a bath when your skin is damp rather than applying steroids to dry skin. If you cover the area with a wet wrap or a bandage, it will help to absorb the medication more. It is important to keep this fact in mind when applying steroids to diaper (nappy) covered skin regions in babies.
Topical steroids can be combined with other active ingredients such as antibiotics, antifungal agent or calcipotriol. Topical Antibiotic/ steroid preparations should be used rarely, short term only. This is to reduce the risk of antibiotic resistance.
Prescribing topical steroids in pregnancy – Mild and moderate potency steroids can be safely used in pregnancy. But if using strong steroids in to large areas or under occlusion, caution should be used because it can get absorbed.
There can be potent steroids illegally present in some cosmetic products sold over the counter or via internet. These can give rise to side effects unknowingly. Always read the label before you try out any new products on your own.
References:
- https://dermnetnz.org/topics/topical-steroid
- https://patient.info/skin-conditions/atopic-eczema/topical-steroids-for-eczema
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK563106/
GET IN CONTROL OF YOUR ECZEMA
Use our AI tool to check the severity of Eczema and keep track of your Eczema progress.