Hand Fungus and Eczema
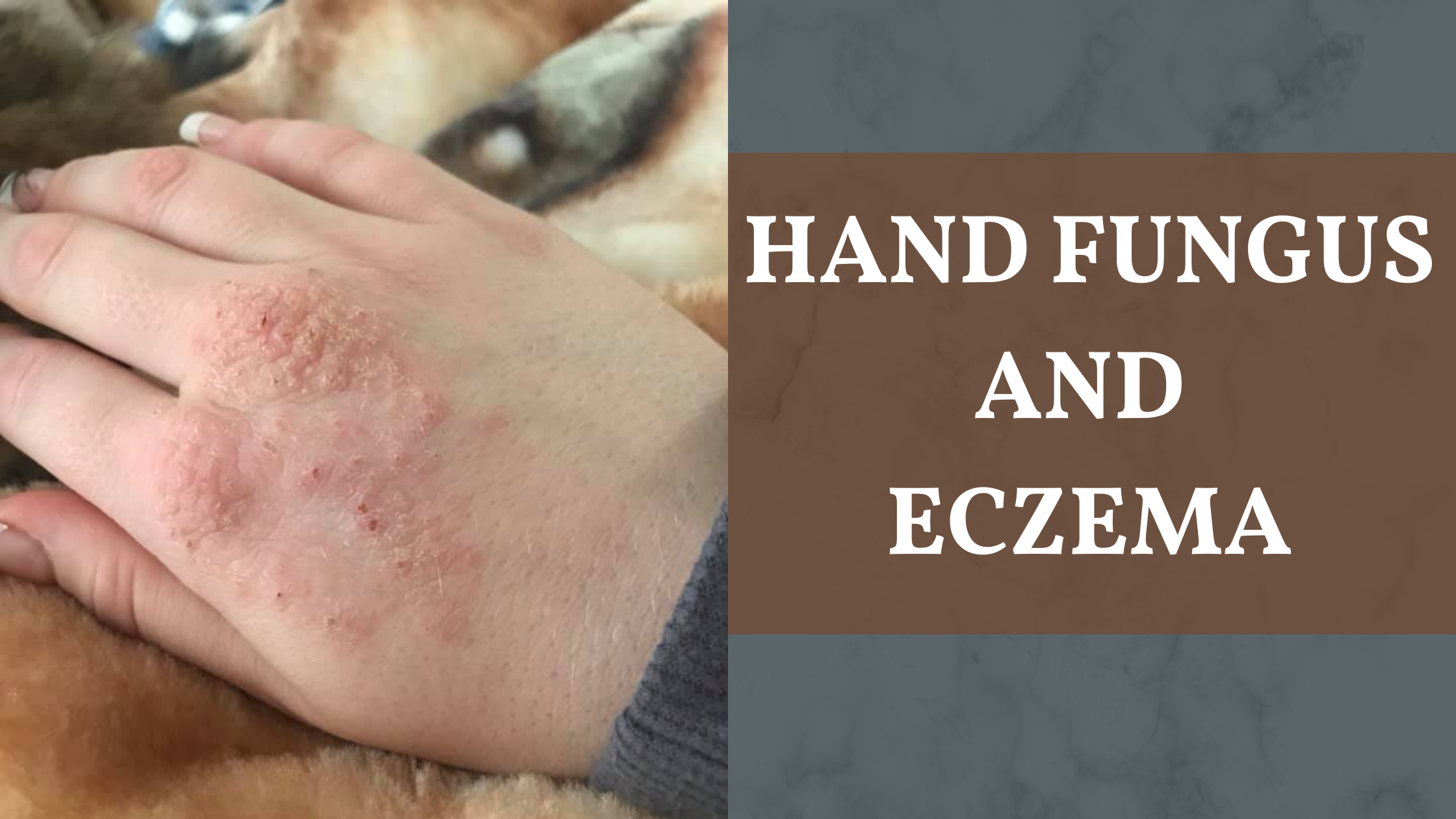
Table of contents
- Introduction
- Hand eczema versus hand fungus?
- What are the risk factors to develop hand fungus?
- What are the causes of hand eczema?
- What are the symptoms of hand fungus?
- Treatment of hand fungus
- Treatment of hand eczema
- Summary
Introduction
Just like you can get fungal infections on your feet, it is possible to develop fungus in your hands. Hand fungus is called ‘Tinea manuum’ but commonly known as ring worm infection. In Tinea manuum, there is a red, scaly rash with a slightly raised border which is shaped like a ring. Commonly you can get it by touching your groin or feet if they are also infected with Tinea or by touching fungus contaminated objects, soil or infected persons. also infected with Tinea or by touching fungus contaminated objects, soil or infected persons. So it is important and get hand fungus treatment.
Sometimes you may falsely identify a hand fungus as hand eczema as they may have certain similarities. Sometimes both these conditions can be associated with each other.
When eczema arises in your hands it is called hand dermatitis or hand eczema. It is a chronic long- lasting skin condition which is also as common as fungal infections. Hand eczema may lead to severe negative effects on the quality of your life and even on your social status. Hand fungus treatment is therefore mandatory.
Eczema or fungus on your hands will be visible as it is difficult to hide, that may be quite embarrassing when you are among others. It will especially affect negatively on people who use their hands for the occupation such as the chefs, attendants and salon workers. Eczema is not contagious, but hand fungus is. Both these skin conditions can be quite severe, but they are not life threatening.
Hand eczema versus hand fungus
Fungal infection and hand eczema may seem similar as both are red, itchy rashes. Hand fungus typically has a raised border commonly with central clearing. The appearance is like a ring. Hand eczema doesn’t have a raised border and middle of the rash does not clear as the rash spread. So there is difference between hand fungus and hand eczema.
Commonly hand fungus affects only one hand, although you may develop it on both hands. Hand eczema is commonly bilateral and symmetrical. Hand eczema can get several flares and remissions while not responding to over the counter antifungal medications. Even after treatment, eczema can only be controlled and can reappear. However, hand fungus will respond to OTC antifungals and may clear off completely if you treat it properly. If partially treated hand fungus can reappear too and if you develop resistance to treatment, the future treatment of the rash will be difficult.
Hand eczema can be genetic and may run in families. Hand fungus is not familial, but often family members can get infected by close contact as it is contagious.
Although hand fungus can sometimes have associated nail involvement, in hand eczema nails are not involved.
What are the risk factors to develop hand fungus?
- Those who do sports that involve close skin contact
- Those using public showers like in gyms etc.
- Sharing things with infected people such as towels, tools
- Those who handle or be around animals as Tinea can spread from animals including cats, dogs and cows.
- Those who wear tight fitting gloves
- If you sweat too much on your hands
What are the causes of hand eczema?
Hand eczema may be related to occupational exposure or house hold activities. It often affects people who are in to catering, cleaning, hair dressing, mechanical work and health care as they frequently come in to contact with chemicals and other irritating substances.
It is a chronic skin condition which is multifactorial. Contact allergens and irritant substances play a role in triggering hand eczema. The exact cause of hand eczema is unknown. There can be a genetic association for hand eczema and it can run in atopic families. Atopy is the genetic tendency to develop allergic conditions like eczema, asthma and hay fever. Stress can be a risk factor for hand eczema.
As hand eczema is not contagious you cannot ‘catch it’ from another person or spread it to others.
Track and Manage your Eczema treatment using a comprehensive Eczema App
Download Eczemaless now
What are the symptoms of hand fungus?
- The infection usually starts on your palm and may spread to other areas like the back of your hands and fingers.
- The rash may start small and get larger gradually with time.
- Itchy, red rash with raised border and the outer surface appears scaly
- Peeling and flaking of the area
- Sometimes the fungus can affect your nails which is called onychomycosis or Tinea unguium. Then your nails can get brittle. They appear discolored, thickened and your nail may get separated from the nail bed.
Sometimes a blistering rash on the edges of your palms and fingers may be caused by the fungi. They appear as crops and will contain a sticky clear fluid. They may have a peeling edge. This rash can itch and burn. The reason why hand fungus treatment is necessary.
What are the symptoms of hand eczema?
- Itching which may be severe – this is a common symptom in almost all hand eczemas.
- If you scratch continuously the rash can become raw, sensitive and swollen.
- Skin lesions are red and inflamed. Swelling can occur due to inflammation.
- The skin of your hand is usually dry and sensitive.
- There can be small raised bumps that may leak fluid.
- Oozing and crusting especially when scratched
- Red or brownish grey dark patches may appear on your hands
- Long standing hand eczema can give rise to leathery, scaly, cracked and thickened lesions.
Treatment of hand fungus
If your hand fungus is mild, you can use an over the counter anti-fungal cream such as micanazole or clotrimazole. If your rash does not respond, seek help from your doctor or a dermatologist. He or she may prescribe a stronger topical anti-fungal agent. A course of oral antifungal medicine will be added if your lesions are severe or when the rash does not respond to topical treatment alone.
You have to make sure that you stick to the treatment regime as incomplete treatment can lead to resistant forms of fungi.
To prevent further fungal infections avoid touching contaminated objects, soil or animals unnecessarily. Do not share towels or other personal items. Avoid using common tools unless it is necessary. Avoid using public showers if possible. All these things comes under hand fungus treatment and therefor important to apply.
Treatment of hand eczema
Unfortunately there is no cure for hand eczema, but you can successfully control it. Try these home remedies to soothe your lesions.
- Avoid scratching as it can worsen hand eczema.
- Identify and avoid triggers that worsen your hand eczema – triggers like pollen, dust, certain foods, strong soaps and detergents,excessive sweating and smoking can worsen hand eczema.
- Avoid strong soaps and detergents. If you must use them, wear gloves to protect your hands. Use cotton gloves when doing chores.
- Use a mild soap or a fragrance free cleanser when bathing and washing hands. Pat dry your hands using a soft towel. Do not rub or wipe hard.
- When you need to clean your hands use lukewarm water instead of hot water.
- Moisturize your hands well with a good emollient. Get a good hand cream to apply frequently in order to prevent them from drying. Make sure to use an emollient that is alcohol and paraben free with minimal fragrance. If you need help to select the best moisturizer that is suitable for your skin, discuss with your doctor or a dermatologist. Apply moisturizer after a bath and soon after washing hands while your skin is still damp. It helps to absorb and lock in moisture.
- You can use cold compresses to help soothe your skin especially if it is raw.
- Over the counter creams like Hydrocortisone can be applied over your lesions. Hydrocortisone is a mild steroid and an anti-itch cream. More potent steroid creams and ointments may be prescribed by your doctor if your lesions are severe (Betamethasone, Mometasone, clobetasol).
- You can try over the counter antihistamines like Fexofenadine, Cetirizine,Chlorpheniramine, or Loritidine to reduce your itching. Read the instruction leaflet prior to taking any OTC medication.
If your hand eczema does not respond to over the counter medications and home remedies, seek help as stronger medications need to be prescribed. If you think that a certain substance at work or home is the culprit behind your eczema, your doctor will do a ‘patch test’ to identify which irritants or allergens are responsible. Your doctor will also discuss the practices and behaviors that may be contributing to your hand eczema and ways to avoid or modify them.
In summary
Hand fungus is clinically differentiated from hand eczema by following signs.
- Most hand fungus affect only a single hand.
- If both your hands are affected, the involvement is not symmetrical.
- Skin markings become white because the surface is scaling. But in hand eczema skin markings will be increased.
- The Tinea rash has a raised border
- Nearby nails can get affected (Tinea unguium)
Hand eczema can get complicated with skin infections. This is because of repeated scratching that destroys your skin barrier leading to cracks and open sores. Skin infections can occur with bacteria, viruses and fungi on a hand with eczema.
When your hand eczema gets a superadded fungal infection, it may give a mixed picture.
The itching will be more as both conditions are known to itch. Scratching can lead to erosions and even oozing. Fungal infection can occur especially when you have wet eczema. Fungus thrives on warm moist skin. Treatment will be difficult as the steroids which are used to treat eczema can worsen the fungal infection. Therefore, oral antifungal medications like Itraconazole or Terbinafine may be needed. Sometimes treatment will take a course of 4-6 weeks to eradicate the fungus. Then the eczema can be controlled with local application of steroids.
References:
https://dermnetnz.org/topics/tinea-manuum
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/9884898/
https://nationaleczema.org/eczema/types-of-eczema/hand-eczema/
GET IN CONTROL OF YOUR ECZEMA
Use our AI tool to check the severity of Eczema and keep track of your Eczema progress.