Natural Treatment for Eczema

Table of Content
What is Eczema?
Eczema is a chronic skin condition that is commonly seen in children. It usually starts in childhood and may continue into adulthood. It can occur in adulthood for the first time, which is called adult-onset eczema. Even the elderly can suffer from eczema. During your lifetime, it can cause several flares and remissions, or it may go into total remission during the teenage years. It is a chronic long-term skin condition.
Eczema is also known as Atopic dermatitis. Atopy runs in families. Therefore, eczema can associate with Bronchial asthma, hay fever (allergic rhinitis), and allergic conjunctivitis (inflammation of the conjunctiva of the eye). Usually, you may find a close relative or a family member suffering from one or more of these conditions.
Eczema is almost always itchy. Itching can be so intense, and it may even disturb your sleep. There are 2 types of Eczemas, wet and dry. In wet-type oozing occurs from lesions followed by crusting. The risk of infection is more in the wet type. The lesions can be raw and angry looking. The dry type has red patches that are associated with dry skin. Lesions can be scaly and cracked.
Constant scratching can gradually thicken the lesions. Sometimes continuous scratching occurs as a habit. You may feel that scratching is soothing and unknowingly may continue to scratch until it bleeds. This may increase the risk of infection as various germs can enter through damaged skin. Continuous scratching in eczema lesions can make it thick, discolored, and leathery.
How can Eczema be treated?
Is there any natural treatment for Eczema? Unfortunately, there is no cure for eczema. It can only be controlled. The aim is to prevent recurrent flares and control the skin condition in remission. Most often Eczema goes into total remission by teenage years and may never reappear.
As we know there are certain trigger factors that can cause and worsen your eczema. Identify these triggers early and avoid them as much as possible. Trigger factors may differ from person to person. Some of the examples for trigger factors include pollen, dust, smoking, fabric dyes, excessive sweating, certain foods, additives and preservatives, strong soaps, and detergents. You might observe that contact with some of these triggers may have a link with your eczema. If you identify triggers the best is to avoid them.
If you are a person living with eczema, you know what it is like to find some relief for your symptoms.
What are the symptoms of Eczema?
- Inflamed red skin
- Dry and sensitive skin
- Itching – which can be severe
- Oozing and crusting in wet type eczema
- Swelling due to inflammation
- Leathery, scaly, and thickened areas after continuous scratching
- Dark patches on the skin
Some of these symptoms are unbearable. Treatment should focus on reducing these symptoms and control the skin condition in remission.
What are the natural treatments for eczema?
Are there any natural treatments for Eczema? Probably you may have already tried a variety of natural products. Some may have worked. But unfortunately, some of them can leave your skin feeling more irritated and even drier.
Here are some tried and tested natural remedies for Eczema which can help to replenish moisture in your skin as well as protect the natural barrier of your skin.
Track and Manage your Eczema treatment using a comprehensive Eczema App
Download Eczemaless now



Colloidal Oatmeal –
Colloidal oatmeal means finely grounded oats which help to soften rough areas of skin and calm inflamed skin. This is a good natural treatment for eczema. You can buy colloidal oatmeal from a drug store or order online. If not, you can prepare your own by grinding oatmeal into a fine consistent powder.
Oatmeal bath for eczema – You may wonder whether this means bathing in a bathtub full of breakfast foods. However, this is not just oatmeal and warm water. Here, the oatmeal is ground into a fine powder which is called colloidal oatmeal. It is suspended in water.
There is a study done in 2012 which showed that colloidal oatmeal protects the skin and soothe the irritation and itching in eczema. The study also indicated that colloidal oatmeal could act as a buffer to help maintain the surface PH of your skin.
Preparation of an oatmeal bath –
- Run lukewarm water into a clean bathtub. Make sure it is warm and not hot because hot water can worsen inflamed skin and draw out moisture from your skin making it drier.
- Add a cup of colloidal oatmeal under the running tap. Mix well with your hand.
- Before getting in, make sure that bathwater is milky and warm.
- Soak for about 10 minutes in the bath. You should feel silky on your skin. This should relieve the itching of eczema too.
- Make sure not to soak too much as it can worsen itching and your eczema.
- Rinse off with fresh lukewarm water. Pat yourself dry with a soft towel. Do not rub yourself as it may worsen irritation and dryness.
- You can apply an emollient afterward to moisturize your skin.
Coconut Oil –
Coconut oil is extracted from harvested mature coconuts. It acts as a natural moisturizer and is a safe and effective natural treatment for eczema. About 50% of the fat content in coconut oil comes from Lauric acid. It is a healthy form of saturated fat, which is also found in breast milk. It has a myriad of health benefits when used topically on your skin or when taken orally.
National Eczema Association claims that coconut oil has antibacterial properties that prevent infection. It reduces staphylococcal bacteria in your skin. Eczematous skin, especially the wet type tends to get infected more, coconut oil can protect it. If you are suffering from eczema, you may notice that patches of inflamed skin can crack and ooze. This is ideal for bacteria to enter and cause infection.
You can apply coconut oil on your skin to obtain benefits such as.
- It is a natural moisturizer which is highly absorbable
- For its antimicrobial properties to protect your skin from infection – it is effective in reducing not only bacteria but also viruses and fungi.
- It hydrates your skin
- Reduces inflammation and pain because it has anti-inflammatory properties. Therefore, coconut oil reduces itching and discomfort associated with your eczema.
- Reduces oxidative stress – A study that is reported in the Journal of Clinical and Diagnostic Research revealed that antioxidants can be beneficial in the treatment of atopic dermatitis/eczema. Virgin coconut oil is rich in antioxidants.
Make sure you choose virgin coconut oil or cold-pressed coconut oil which is processed without chemicals. Coconut oil may not cure your eczema, but it is effective to reduce eczema symptoms by soothing your skin and easing the irritation and itching.
However, here are some cautions.
- If you are allergic to coconuts, do not use its oil on your skin.
- If you are already on prescription medicines for your eczema, check with your doctor regarding using coconut oil as an adjunct to your treatment.
How do you use coconut oil?
Put a little bit of virgin coconut oil on your hands and rub them together. Apply liberally on your skin when it is slightly damp. You can use it twice a day. Having coconut oil on your skin overnight helps maximum absorption.
Evening Primrose Oil (EPO) –
Evening Primrose Oil is extracted from the seeds of the flower of the evening primrose plant. It can be used topically as well as orally for its healing benefits. When used topically, it can soothe your irritated skin. When taken orally, it can treat systemic inflammatory conditions like eczema.
Evening Primrose Oil contains Omega 6 fatty acids and gamma Linolenic acid which prevent inflammation in your body. It helps to reduce eczema symptoms without negative side effects. Some countries have approved Evening Primrose Oil as a treatment for eczema and other inflammatory skin conditions.
How to use it?
- 1 to 4 capsules can be taken by mouth twice a day for 3 months.
- Topically apply 20% Evening Primrose oil on affected areas of skin twice a day
However, research is not adequate, and many of these studies show mixed results. Evening Primrose Oil may work in some of you with eczema. Since side effects are rare, there is no harm in trying it as a natural remedy. But check with your doctor first before you start using it.
Witch Hazel –
Witch Hazel is an astringent or toner made from the leaves and bark of the Witch-hazel shrub. It is indigenous to the United States and it is used for centuries by Native Americans for many skin ailments. It has been used for many years as a topical treatment for eczema and other types of skin inflammation. It is known to soothe inflamed skin, relieve itching, and even dry up oozing lesions.
However, research on the effects of Witch hazel on eczema is rare.
How do you use it?
Witch Hazel can be bought in its pure form at local drug stores. You can apply it topically over the affected skin. Since the safety of this ingredient is not studied widely, it is always better to discuss with your dermatologist first.
Aloe vera gel –
It is derived from the leaves of the aloe vera plant. Aloe vera gel has antimicrobial, wound healing, and immune system boosting properties. It can be used to soothe eczematous skin.
Aloe vera gel can be bought in drug stores and online. You can even extract the gel yourself from the leaves of the plant. Applying aloe vera gel on your skin is found to be safe and effective in both children and adults.
Sunflower oil –
Sunflower oil is extracted from the sunflower seeds. Studies have shown that sunflower oil protects your skin’s outer layer (epidermis) which is the natural barrier.
It helps to keep the moisture in and prevents bacteria from entering. Sunflower oil is known to hydrate your skin. It can relieve itching and inflammation in eczematous skin.
How to use it?
You can apply undiluted sunflower oil directly on your skin, especially in affected areas. It absorbs well when your skin is still damp after a bath.
Calendula Oil and cream –
Calendula oil is a natural oil extracted from marigold flowers. It has anti-inflammatory, antibacterial, and anti-fungal effects. It is a natural herbal remedy. Calendula has been used for centuries to heal skin inflammations as well as cuts and burns.
It is known to improve your blood circulation to areas of inflammation and injury. Calendula helps to hydrate skin and fights off skin infections.
It is available in local drug stores and online. It may work in some of you with eczema, although research is lacking in its effectiveness. It is generally safe to use. Avoid it, if you are allergic to Marigold plants and if you are pregnant or breastfeeding.
There are some other natural remedies for eczema that you can try such as Acupuncture and Acupressure.
How are Acupuncture and Acupressure effective for treating eczema?
Acupuncture is an ancient Chinese medicine used to treat a variety of disease conditions. It has been studied and practiced for more than 2500 years. The acupuncture practice is done using fine needles which are inserted into specific points in your body. This triggering of certain points is known to alter the flow of energy. For some of you, the thought of getting needles inserted into your body may be terrifying, but some claim that it is effective in relieving their symptoms and it is not that painful. Research is not adequate for its effectiveness in treating eczema, however, some believe that it can relieve the itch.
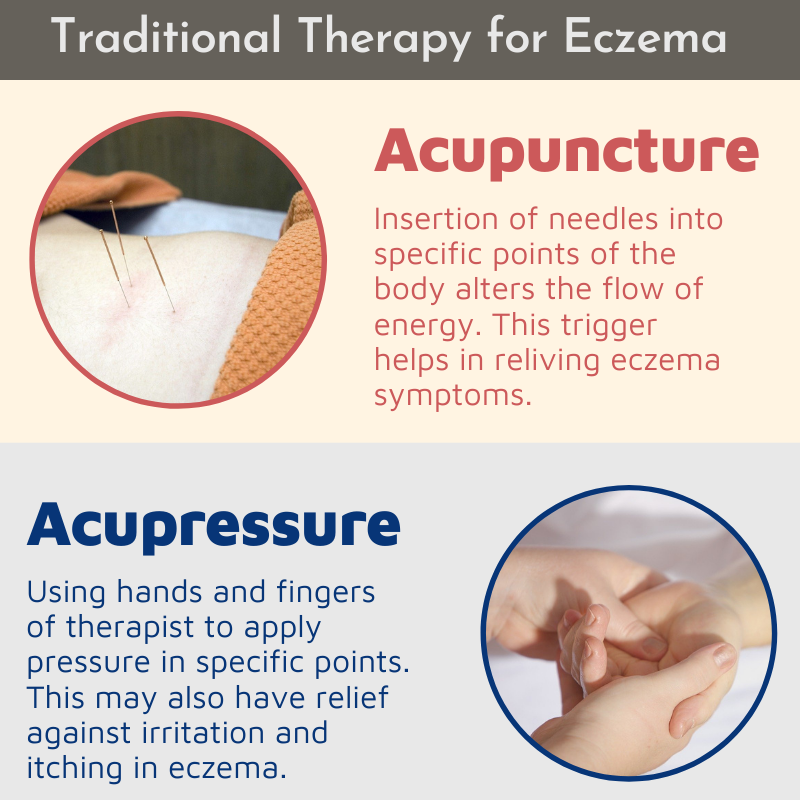


Acupressure uses the hands and fingers of the therapist to apply pressure instead of using needles. This may also have relief against irritation and itching in eczema.
Bath therapy
Having a long bath twice a day helps to keep your skin hydrated. Make sure you apply an emollient soon after your bath to lock in moisture.
Practicing relaxation techniques to fight stress
Stress is a well-known trigger for eczema. Stress plays a role in developing inflammation not only on the skin but also in other parts of your body. So, if you learn to manage stress and cope with stressful situations in life, you can reduce eczema flare-ups.



Here are some relaxation techniques you can practice to reduce stress.
- Yoga – It is a way of life that can develop discipline, self- inquiry, and non- attachment in you. Yoga improves your health, flexibility, and empower you with conscious choices while fulfilling you with peace, clarity, and happiness.
- Meditation – Meditation is learning how to pay attention to mindfulness. It can give you a sense of calm, peace, and balance while improving your emotional health as well as your overall well- being.
- Cognitive-behavioral therapy – This is a therapy that identifies and changes potentially self- destructive and unhealthy behaviors.
- Deep breathing – Being mindful about your breathing pattern helps to relax your mind.
- Music therapy – Use of music to address physical, emotional, cognitive, and social needs. You can listen to melodies, play an instrument, write a song, or guided imagery as music therapy.
- Hypnosis – Hypnosis creates a state of focused attention during which positive suggestions and guided imagery are used to help the individual.
- Tai chi – It is a Chinese tradition with martial arts that involve slow movements and deep breaths.
- Visualization – Using art therapy and visual imagery as a way of positive communication.
- Biofeedback – Biofeedback is a type of therapy that uses sensors that are attached to your body to measure the key body functions. It helps to learn how your body works.
- Massage – it improves the blood flow to your skin. Massages are known to reduce stress and anxiety.
If you practice relaxation techniques regularly, your stress levels will fall. With time you will notice that there is an improvement in your skin too.
As you can see, there are many tried and tested natural remedies to treat eczema. They may not be effective for all especially if your eczema is widespread and severe. But for some of you, these natural treatments will work wonders in soothing your skin and reducing the symptoms of your eczema.
However, if you are on prescription medications for your eczema, it is better to check with your dermatologist or your doctor, before you try natural home remedies.
There are certain home remedies we can try to treat and to prevent eczema.
- Avoid strong soaps and detergents as they worsen eczema. Use mild soap when bathing. Pat dry your skin with a soft towel and never rub or wipe hard as it strips away the moisture of your skin.
- Moisturizing your skin well with a good emollient is a must. This must be done several times a day. You should choose an emollient which is paraben and alcohol-free with minimal fragrance. A few examples of ingredients in a good moisturizer are aqueous cream, cocoa butter, Shea butter, Argon oil, glycerol, Dimethicone, and Lanolin Oil. When you select a moisturizer always read the label and check for the ingredients. Avoid creams with ingredients that you are allergic to. Choose the best emollient which is suitable for your skin.
- Apply moisturizer after a bath when your skin is still damp. It helps to absorb and lock in the moisture.
- Scratching worsens your eczema. Eczema is known as “The itch that rashes”, that means the rash appears following itching and worsen once the person scratches. Therefore, you should avoid scratching by all means.
Natural treatment for eczema may not work for all. Usually, it is effective in mild forms of eczema. You may even combine natural treatments with other known treatment options. There is no harm in using an over the counter cream like hydrocortisone which is a mild steroid over the lesions. Using an over the counter antihistamine like Fexofenadine, Cetirizine, Loratadine or chlorpheniramine will reduce itching and your urge to scratch. Make sure that the dose of the medicine and frequency of administration is right.
If you live with eczema, avoid anything which can irritate or dry up your skin which can lead to a flare-up. Perfumes, wool clothing, tight-fitting clothes may be such irritants.
It is also known that food allergies are a common cause of eczema, especially in children. Common foods that are linked to eczema are eggs, soy, wheat, milk, seafood, and peanuts. Try to eliminate some of these and see whether there is an improvement in your eczema.
Why do people seek alternative treatments for eczema?
People tend to seek alternative treatment for eczema such as natural remedies because there is simply no cure for this disease, and no one knows the exact cause of eczema. The outcome of conventional eczema treatments may not be always consistent and not always perceived as safe. There are many side effects of long-term application of topical corticosteroids as well as oral medications used in eczema.
So, many of you with eczema may wonder what natural remedies have to offer when it comes to eczema management. Alternative medicines are natural remedies that people talk about and use, even though many of them are found not to work in research studies. In fact, some people claim that natural treatments have an impact on controlling their eczema. Therefore, one should carefully weigh the pros and cons before starting any natural treatment. The best is to discuss it with your doctor.
You can use natural products, creams, dietary, and lifestyle changes to control and prevent eczema flares, especially in the winter season when symptoms are at their worst. What you should remember is just like conventional treatments, natural remedies cannot cure eczema, but they can help to manage your symptoms to a certain extent and even prevent flares if you believe in them.
When should you seek help?
If your eczema doesn’t answer the home remedies and these natural treatments, you use or if it worsens with time and it worries you it is time to seek help. Your doctor will prescribe topical steroids as well as oral treatments to control the lesions. Always ask whether it is alright to continue the natural treatment methods along with the prescribed medicine.
References:
- https://www.healthline.com/health/natural-remedies-to-reduce-eczema-symptoms
- https://www.healthline.com/health/oatmeal-bath-for-eczema
- https://www.healthline.com/health/calendula-oil
- https://www.healthline.com/health/acupuncture-how-does-it-work-scientifically
- https://nationaleczema.org/alternative-treatments/
GET IN CONTROL OF YOUR ECZEMA
Use our AI tool to check the severity of Eczema and keep track of your Eczema progress.