Behcet’s Disease is a rare, chronic disorder that results in blood vessel inflammation throughout the body. This systemic condition, also known as Behcet’s Syndrome, can lead to numerous symptoms affecting various organs and systems. While the exact cause of Behcet’s Disease remains unknown, its impact can be severe, necessitating prompt diagnosis and comprehensive management. This article delves into the symptoms, causes, and treatment options for Behcet’s Disease, providing a detailed overview for those seeking information about this complex condition.
Behcet’s Disease manifests in a wide range of symptoms, making it a multifaceted condition that can affect multiple parts of the body. The most common symptoms include:
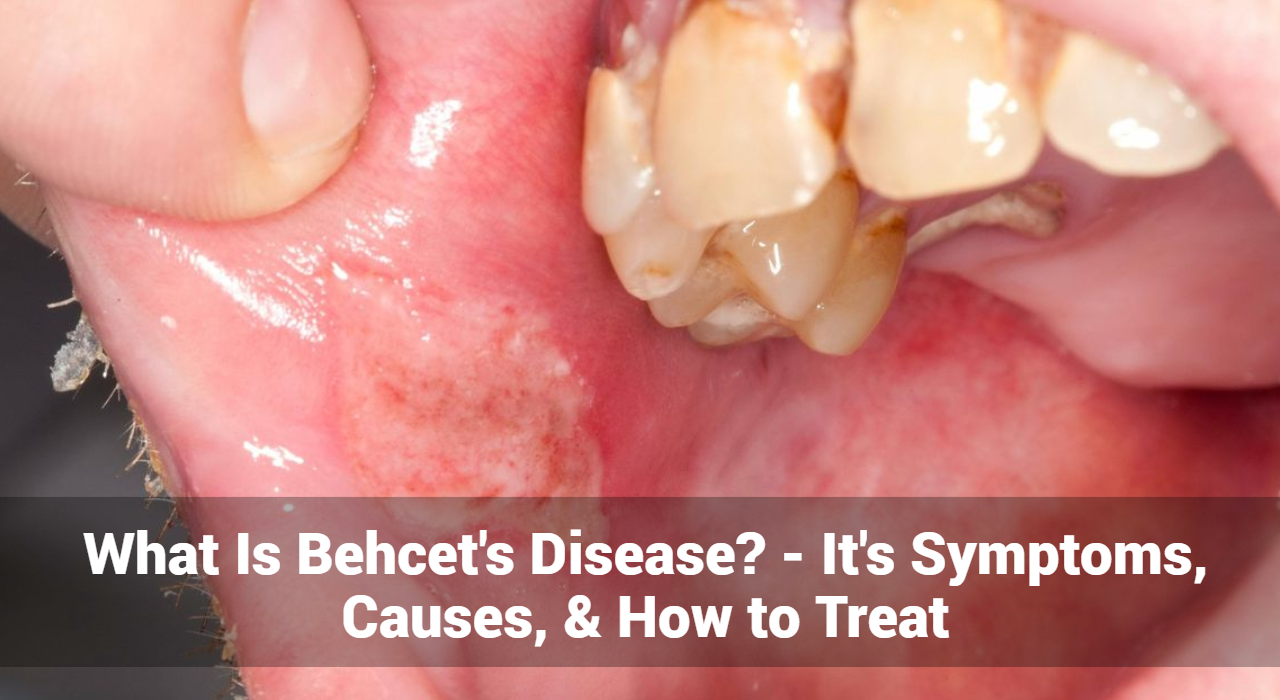
- Oral Ulcers: One of the hallmark symptoms of Behcet’s Disease is the presence of painful mouth sores, which often resemble canker sores. These ulcers can recur frequently and cause significant discomfort.
- Genital Ulcers: Similar to oral ulcers, genital sores are another common symptom. These painful lesions can appear on the scrotum in men and the vulva in women, and they tend to recur.
- Skin Lesions: Skin problems associated with Behcet’s Disease can vary. Common manifestations include acne-like sores, red nodules, and erythema nodosum, which are tender, red bumps usually found on the legs.
- Eye Inflammation: Behcet’s Disease can cause various forms of eye inflammation, including uveitis, which can lead to redness, pain, and blurred vision. If left untreated, it can result in vision loss.
- Joint Pain: Many individuals with Behcet’s Disease experience joint pain and swelling, particularly in the knees, ankles, elbows, and wrists. This can significantly impact mobility and quality of life.
- Gastrointestinal Symptoms: Behcet’s Disease can also affect the digestive system, leading to abdominal pain, diarrhea, and, in some cases, gastrointestinal bleeding.
- Neurological Symptoms: Although less common, Behcet’s Disease can involve the central nervous system, causing headaches, confusion, strokes, and symptoms similar to meningitis.
- Vascular Symptoms: Inflammation of veins and arteries can occur, potentially leading to blood clots, aneurysms, and other serious complications.
What Causes of Behcet’s Disease?
The exact cause of Behcet’s Disease is not fully understood, but several factors are believed to contribute to its development:
- Genetic Factors: Genetics play a significant role in Behcet’s Disease. Certain genetic markers, such as HLA-B51, are associated with an increased risk of developing the condition. However, not all individuals with these markers will develop Behcet’s Disease, indicating that other factors are also involved.
- Immune System Dysfunction: Behcet’s Disease is considered an autoimmune disorder, where the immune system mistakenly attacks the body’s own cells and tissues. This abnormal immune response leads to widespread inflammation and the characteristic symptoms of the disease.
- Environmental Triggers: Environmental factors, such as infections or exposure to certain bacteria or viruses, may trigger Behcet’s Disease in genetically predisposed individuals. Research is ongoing to identify specific environmental triggers that could initiate the disease process.
GET IN CONTROL OF YOUR ECZEMA
Use our AI tool to check the severity of Eczema and keep track of your Eczema progress.
How to Treat Behcet’s Disease?
While there is no cure for Behcet’s Disease, several treatment options can help manage its symptoms and improve the quality of life for those affected. Treatment plans are typically tailored to the individual’s specific symptoms and may include:
- Medications:
- Corticosteroids: These anti-inflammatory drugs are often used to control acute flare-ups of Behcet’s Disease. They can be taken orally or applied topically to reduce inflammation and alleviate symptoms.
- Immunosuppressants: Medications like azathioprine, methotrexate, and cyclophosphamide help suppress the immune system, reducing the frequency and severity of flare-ups.
- Biologics: TNF inhibitors such as infliximab and adalimumab are used to target specific parts of the immune system. These drugs can be effective in treating severe cases of Behcet’s Disease.
- Colchicine: Commonly used for treating gout, colchicine can also be effective in managing the symptoms of Behcet’s Disease, particularly skin and joint symptoms.
- Lifestyle Adjustments:
- Regular Exercise: Engaging in regular physical activity can help maintain joint function and overall health. Low-impact exercises like swimming and walking are often recommended.
- Healthy Diet: A balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins can support overall health and well-being. Some individuals may need to adjust their diet based on gastrointestinal symptoms.
- Stress Management: Stress can trigger flare-ups in some individuals with Behcet’s Disease. Techniques such as meditation, yoga, and mindfulness can help manage stress levels.
- Regular Monitoring: Ongoing medical care is essential for managing Behcet’s Disease. Regular check-ups with a healthcare provider can help monitor symptoms, adjust treatment plans, and prevent complications.
Diagnosis
Diagnosing Behcet’s Disease can be challenging due to its diverse symptoms and the lack of specific tests. Diagnosis is usually based on clinical criteria, including the presence of recurrent oral ulcers along with at least two other symptoms, such as genital ulcers, eye inflammation, skin lesions, or a positive pathergy test (a skin reaction to a minor injury).
Conclusion
Behcet’s Disease is a complex and multifaceted condition that requires a comprehensive approach to management. Understanding its symptoms, causes, and treatment options is crucial for those affected and their caregivers. While there is no cure, advancements in medical research and treatment options offer hope for better management and improved quality of life for individuals with Behcet’s Disease. Early diagnosis, personalized treatment plans, and lifestyle adjustments can make a significant difference in living well with this chronic condition.
Track and Manage your Eczema treatment using a comprehensive Eczema App
Download Eczemaless now