Kawasaki Disease, also known as Kawasaki Syndrome, is a rare but serious condition that primarily affects children. It is characterized by inflammation of the blood vessels throughout the body, leading to a range of symptoms that can have significant long-term effects if not addressed promptly. Understanding the symptoms, causes, and treatment options for Kawasaki Disease is crucial for parents, caregivers, and healthcare professionals alike.
What is Kawasaki Disease?
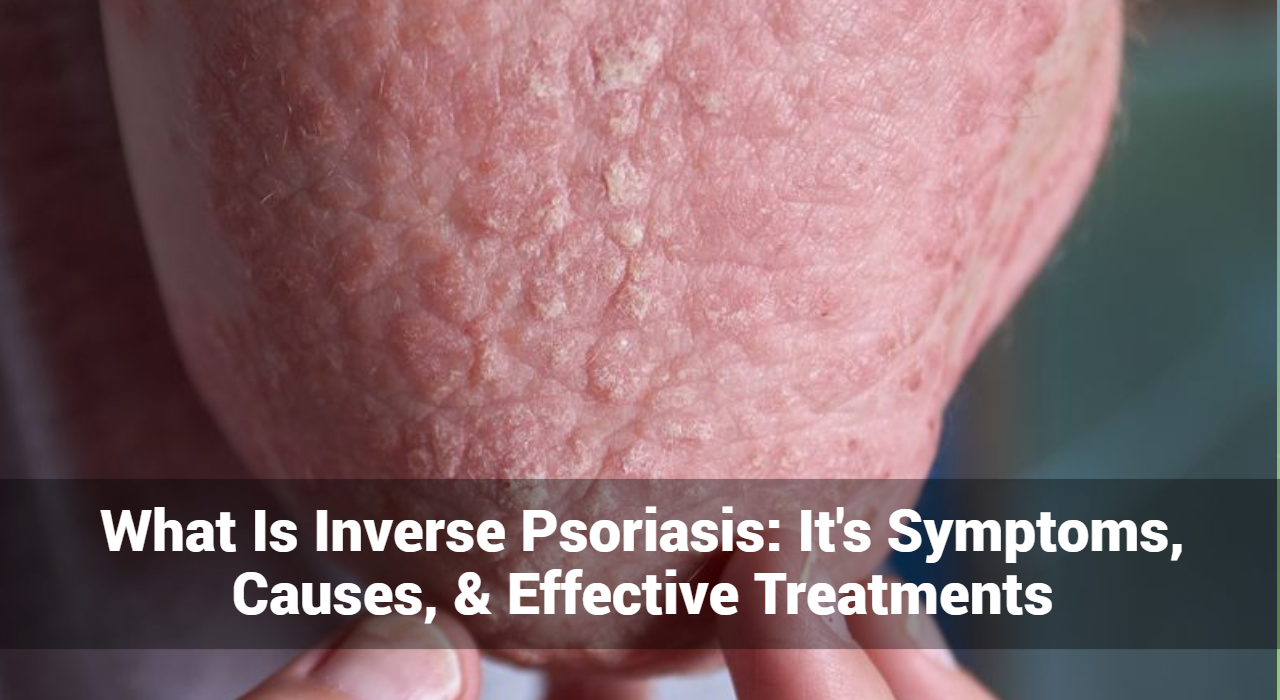
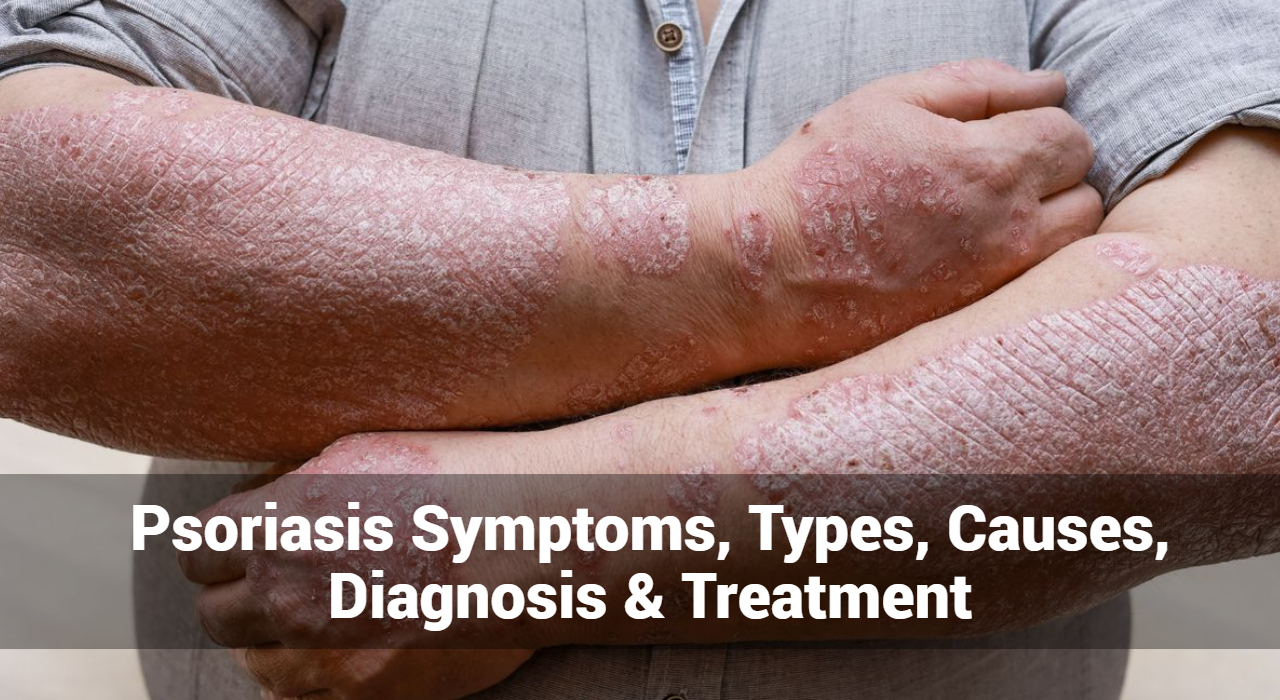
Kawasaki Disease is an autoimmune skin condition that causes inflammation in the walls of medium-sized arteries, including those in the heart. It primarily affects children under the age of five and can lead to serious complications if not treated promptly. The disease was first identified by Dr. Tomisaku Kawasaki in Japan in the 1960s, and it has since been recognized globally.
What Are Symptoms of Kawasaki Disease?
The symptoms of Kawasaki Disease typically occur in phases and can vary from child to child. Early recognition and treatment are crucial to prevent complications. Here are the common symptoms associated with Kawasaki Disease:
1. Fever: One of the earliest signs of Kawasaki Disease is a high fever lasting more than five days, often reaching temperatures of 102°F (38.9°C) or higher. The fever may come and go, and it is usually unresponsive to standard antipyretic medications.
2. Rash: Children with Kawasaki Disease often develop a rash that may cover large areas of the body. The rash can be red, bumpy, and may appear on the trunk, arms, and legs. It often resembles a measles-like rash and can vary in appearance.
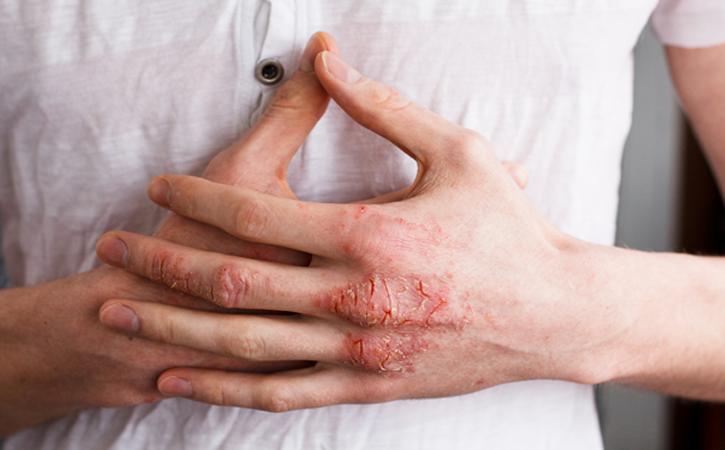
3. Swollen Hands and Feet: Swelling of the hands and feet is another common symptom. The skin may appear red and swollen, and the child may experience discomfort and difficulty moving their limbs.
4. Conjunctivitis: Conjunctivitis, or redness and inflammation of the eyes, is frequently observed in Kawasaki Disease. The eyes may appear red and watery, but there is usually no discharge or crusting.
5. Strawberry Tongue: A distinctive symptom of Kawasaki Disease is a “strawberry tongue,” characterized by a bright red, swollen tongue with prominent taste buds. This appearance is often coupled with cracked and dry lips.
6. Swollen Lymph Nodes: Swelling of the lymph nodes, particularly those in the neck, can occur. This swelling is usually painless but can be noticeable and tender.
7. Irritability and General Malaise: Children with Kawasaki Disease may exhibit irritability and general discomfort. They may also experience joint pain and stomach pain, contributing to their overall malaise.
Track and Manage your Eczema treatment using a comprehensive Eczema App
Download Eczemaless now
What Causes of Kawasaki Disease?
The exact cause remains unknown, but several factors are believed to contribute to its development:
1. Genetic Factors: Genetics may play a role, as it tends to occur more frequently in certain populations. Children of Asian descent, particularly those of Japanese or Korean heritage, have a higher incidence of the disease.
2. Infections: Some researchers suggest that infections, such as viral or bacterial infections may trigger Kawasaki Disease. However, no specific pathogen has been conclusively linked to the disease.
3. Immune System Response: Kawasaki Disease is considered an autoimmune condition, where the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks its own blood vessels. This abnormal immune response leads to inflammation and damage to the arteries.
4. Environmental Factors: Environmental factors, such as exposure to pollutants or certain chemicals, may also play a role in the development of Kawasaki Disease. However, these factors have not been definitively proven to cause the condition.
Diagnosis of Kawasaki Disease
Diagnosing Kawasaki Disease can be challenging due to its overlapping symptoms with other illnesses. Healthcare professionals use a combination of clinical criteria and diagnostic tests to confirm the diagnosis:
1. Clinical Criteria: Diagnosis is primarily based on clinical criteria, including the presence of fever lasting more than five days along with at least four of the following symptoms:
- Rash
- Swelling of hands and feet
- Conjunctivitis
- Strawberry tongue
- Swollen lymph nodes
2. Laboratory Tests: Blood tests may be conducted to assess inflammation markers, such as erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) or C-reactive protein (CRP). Elevated levels of these markers can support the diagnosis of Kawasaki Disease.
3. Imaging Studies: Echocardiography (ultrasound of the heart) is used to evaluate any potential damage to the heart or coronary arteries. This helps in assessing the risk of complications such as coronary artery aneurysms.
GET IN CONTROL OF YOUR ECZEMA
Use our AI tool to check the severity of Eczema and keep track of your Eczema progress.
What Are The Treatment of Kawasaki Disease?
Early treatment is crucial to reduce the risk of complications and improve outcomes. The primary goals of treatment are to reduce inflammation, prevent damage to the heart, and alleviate symptoms. Treatment options include:
1. Intravenous Immunoglobulin (IVIG): Intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG) is the primary treatment for Kawasaki Disease. It is administered through an intravenous drip and helps reduce inflammation, lower fever, and prevent coronary artery damage. The treatment is most effective when given within the first ten days of the illness.
2. Aspirin: Aspirin is used in conjunction with IVIG to help reduce inflammation and fever. It also plays a role in preventing blood clot formation and reducing the risk of coronary artery complications. The dosage and duration of aspirin therapy are carefully managed by healthcare professionals.
3. Steroids: In some cases, corticosteroids may be prescribed if the initial treatment with IVIG and aspirin is not effective. Steroids help control inflammation and can be beneficial in severe cases of Kawasaki Disease.
4. Supportive Care: Supportive care includes managing symptoms and providing comfort measures. This may involve hydration, pain management, and monitoring for any potential side effects of treatment.
5. Long-Term Follow-Up: Regular follow-up appointments are essential to monitor the child’s heart health and ensure there are no long-term complications. This may include periodic echocardiograms to assess the condition of the coronary arteries.
Complications of Kawasaki Disease
Without timely and appropriate treatment, Kawasaki Disease can lead to several serious complications:
1. Coronary Artery Aneurysms: The most significant complication of Kawasaki Disease is the formation of aneurysms in the coronary arteries. These aneurysms can lead to long-term heart problems, including heart attacks and reduced heart function.
2. Myocarditis: Inflammation of the heart muscle (myocarditis) can occur, leading to weakened heart function and potential heart failure.
3. Heart Valve Issues: In some cases, Kawasaki Disease can affect the heart valves, leading to valvular dysfunction or regurgitation.
4. Long-Term Cardiovascular Risk: Children who have had Kawasaki Disease may be at increased risk for cardiovascular issues later in life. Ongoing monitoring and management are essential to mitigate these risks.
Conclusion
Kawasaki Disease is a serious condition that requires prompt recognition and treatment to prevent complications. Understanding the symptoms, causes, and available treatments can help ensure that affected children receive the care they need. If you suspect your child may have to seek medical attention immediately to receive a timely diagnosis and appropriate treatment. With early intervention, many children recover fully and lead healthy lives.
For more information, consult a dermatologist to stay informed about the latest research and treatment options.
Track and Manage your Eczema treatment using a comprehensive Eczema App
Download Eczemaless now