Table of Content
Introduction:
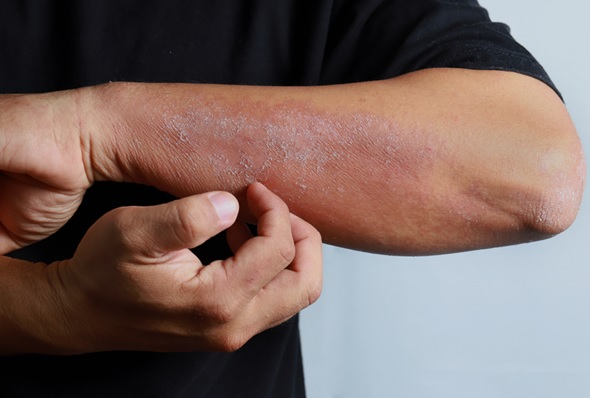
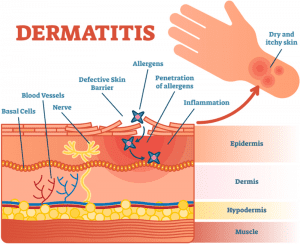
Atopic Dermatitis or as commonly known as Eczema is all about a skin condition that becomes abnormal developing cracks, bumps, red, the skin loses its ability to withhold the moisture thus becomes dry and itchy. The skin barrier becomes weak allowing certain microbes to enter leading to an immune response resulting in inflammation. This Microbes in some cases worsens the condition developing various infections in eczema. Most of the eczema treatment and care plans are external with steroids and topical treatment plans as suggested by the physician subject to the patient’s condition. But in many cases elimination of certain food categories or ingredients drastically improves the condition. This is because food may act as a trigger in resulting in eczema flare-up. But how could a food which doesn’t make any contact with the external skin like other triggers (cloth, weather, dust, etc. do) has an impact on the skin. Well, this could be due to the phenomenon which we will discuss ahead know as “Leaky gut syndrome”.
Overall identifying triggers that flares of your eczema play a critical role, manage them using an AI eczema app and keep your triggers under check.
What is the Gut?
The gut is one of the vital disease-fighting systems of the human body. Many of the body’s immune cells are located in the gut and the microbes are deeply intertwined with the immune system
Similar to the skin which acts as a barrier preventing the foreign particles to enter the body, our intestine has an extensive lining that forms a tight barrier or junctions. These tight junctions form the gateway between the intestine and bloodstream, which controls, which substance should be allowed to enter.
The main job of this junction is to maintain a balance between allowing vital nutrients to enter your bloodstream, but still remaining small enough to prevent other hazardous disease-causing substances from passing out of your digestive system into the rest of your body.
What does Leaky Gut Syndrome mean?
When this tight barrier gets disrupted, the junction becomes loose developing cracks or holes, allowing very tiny undigested food particles, metabolic waste toxins, and other microbes to penetrate the tissues beneath it and enter the bloodstream. This triggers the inflammation and, in many cases, also causes the changes in gut flora (friendly microbes) that could lead to many problems like an autoimmune response.
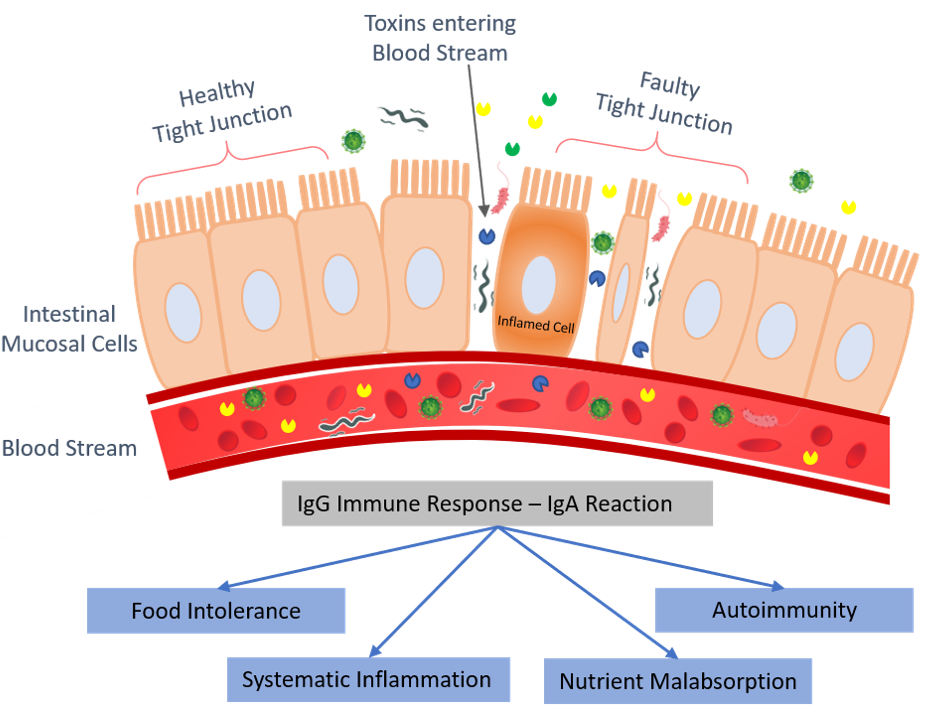


An immune response from your immune system which is so normal that serves to fight infections and diseases, now fighting your own cells leading to chronic inflammation, which is a root cause of major diseases like eczema, asthma, autism and the list goes on.
This action of immune response due to the disrupted intestine lining is called Leaky Gut Syndrome. In medical literature, a leaky gut is also referred to as “intestinal hyperpermeability.”
Leaky Gut and Eczema
According to research noted down in the Journal of Investigative Dermatology with a subject Increased intestinal permeability in atopic eczema. A research study was conducted on 26 children with eczema which concluded that 14 of the participants had leaky gut and eczema. The researchers said that leaky gut was likely caused by food intolerances so elimination diets were undertaken by many of the participants.
So does that mean that the main reason is undiagnosed food intolerance?
Well, Often it could be. But sometimes it’s not – remember eczema is not caused by one single issue, it can be different for different individuals.
More studies are required to determine if leaky gut is universal in atopic dermatitis or if there are specific subtypes/phenotypes for which it is relevant says Peter A. Lio, M.D. Assistant Professor of Clinical Dermatology North-western University Feinberg School of Medicine.
So leaky gut could be one of the reasons for Eczema but not every eczema is caused by Leaky gut syndrome
An unhealthy Gut means a low immune system and thereby even a small trigger or other factors make you fall sick in eczema causing eczema flare.
What causes Leaky Gut?
Though the clear cause of Leaky gut is mysterious, however, it was found that the following reasons may increase the intestinal permeability.
- High Gluten consumption
- Infections like candida, intestinal parasites, and small intestine bacterial overgrowth (SIBO)
Both Gluten and overgrowth of bacteria stimulate higher levels of a protein called zonulin, which is known to regulate tight junctions and an increased level of this protein may loosen tight junction causing leaky gut
- Excess consumption of inflammatory foods
- Long term use of Antibiotics or non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) such as Aspirin may also cause intestinal permeability
- Low levels of Healthy Gut Bacteria
Track and Manage your Eczema treatment using a comprehensive Eczema App
Download Eczemaless now
Diagnosis
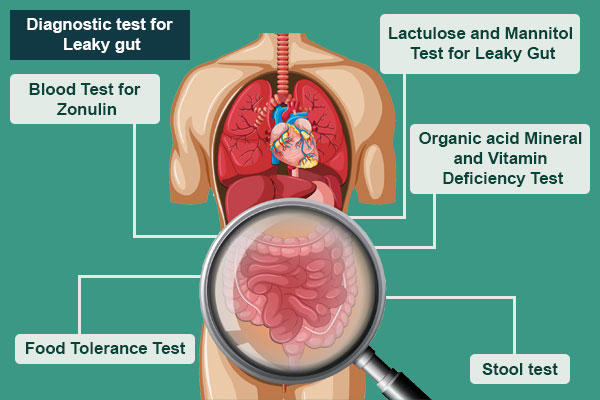


Although there are no Diagnosis for Leaky Gut Syndrome that is thought in the school of medicine which can tell you how leaky is your gut, there are certain factors which can be tested to find the condition indirectly
- Lactulose and Mannitol Test for Leaky Gut
This test analyzes urine for the clearance of two sugars, lactulose, and mannitol, which are by-products of the leaky gut syndrome. The patient has to consume these sugars and the ratio of Lactulose to mannitol ratio in the urine.
- Organic acid Mineral and Vitamin Deficiency Test
Nutrient Malabsorption or vitamin/ mineral deficiency are some of the serious warnings that you may have leaky gut. The organic acid test helps identify nutritional deficiencies. - Blood Test for Zonulin
As discussed earlier of Zonulin effects the opening of the tight junctions so the Increased amount of Zonulin shall cause the Tight junction to loosen resulting in intestinal permeability. A blood test is to identify the amount of Zonulin level in the blood. - Stool test
Just like blood test is done to see what’s wrong in the with the organs. Stool test is done to analyze the condition of the Gut. They’ll look for bacteria (good and bad), viruses, bacteriophages, fungi, yeast, parasites and all sorts of other goodies that may be contributing to my intestinal permeability, aka leaky gut. - Food Tolerance Test
Although it may not help in the direct diagnosis of the leaky gut, once you diagnosed with leaky gut this test plays an important role to plan your diet and to list out which food or ingredients have to be avoided. These tests are also available as a dried blood spot collection.
Signs and symptoms of Leaky gut syndrome
Symptoms may not be the same for everyone it may differ from person to person and one may have a combination of symptoms which may include
- Stomach pains, especially after eating due to undigested particles breaching the tight junction and entering the bloodstream leading to immune response
- Chronic diarrhea, constipation, gas or bloating, inflammatory bowel disease
- Nutritional deficiencies may occur due to improper absorption of Nutrients
- The Immune system weakens and a person fall sick more frequently
- The person may suffer from Headaches, brain fog, memory loss, and Excessive fatigue
- Skin rashes and problems such as acne, eczema, or rosacea may develop due to inflammation.
- The person craves for sugar or carbs due to loss of sugar in Urine
- Arthritis or joint pain
- Depression, anxiety, ADD, ADHD
- Autoimmune diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis, lupus, celiac disease or Crohn’s
- Food Allergies are believed to be one of the most common leaky gut symptoms.
- leaky gut has been shown to cause various neurocognitive disorders causing Mood issues and autism in some cases
Treatment



Whenever a person falls sick it is a common habit to change the diet may it be for a small period of time as short as a couple of days. The treatment for Leaky Gut revolves around a Healthy selective diet eliminating the foods that your body treats as toxic and Gut repairing supplement. the digestive tract is a key player in the manifestation of eczema, psoriasis, and allergy symptoms.
Remove foods that cause inflammation
A common initial step most of the practitioner’s advice is to remove foods that can be inflammatory. Among the most common are
- Alcohol and Carbonated Beverages
- Caffeine
- Dairy products
- Baked goods
- Gluten-containing products and Grains
- Sauces
- Refined Oils
- Artificial Sweeteners
- Mushrooms
- Nuts
- Potatoes and Tomatoes
- Any kind of processed foods, (especially canned foods)
- Certain medications,
- Any foods that may cause allergies or sensitivities.
Nutrients that repair the gut lining and protect it from injury are required to heal the leaky gut. Hence Eczema Diet and Eczema Detox programs have a great success rate.
Incorporate foods that have an anti-inflammatory effect
- Bone Broth is rich in amino acids and minerals with gut-healing collagen providing perfect nourishment for the inflamed gut.
- Turmeric’s anti-inflammatory property helps with the inflammation occurring in the gut lining and also acts as detox.
- Coconut products such as coconut oil, milk, dried coconut, coconut water. Coconut helps fight the overgrowth of bacteria, yeast and fungus in the gut.
- Fermented foods and vegetables like kimchi and sauerkraut bring good bacteria into the gut.
- Choose a wide variety of colorful vegetables and fruits with plenty of leafy greens. Every diet should be “plant-based”.
- Fruits with Low Glycaemic Index
- Sprouted seeds (like chia seeds, flaxseeds, and hemp seeds)
- Herbal teas
- Olives and olive oil (Avoid deep frying)
Most of the eczema sufferers get eczema when they consume high salicylate-containing food. An eczema diet including a low salicylate broth are gentle on the gut and good for the skin specially to those who are sensitive to salicylate
Probiotic therapy
The best way to improve the gut is to keep the gut bacteria healthy by means of diet i.e. consume probiotics. Studies have shown that an increase of probiotic or cultured foods can help in nourishing good bacteria. Incorporate Vitamins B6 and C in diet or via supplements, which are very beneficial to help the gut lining to repair.
Probiotic supplements are generally safe and are potentially effective means of decreasing immune system triggers and improving eczema symptoms. Probiotic bacteria are thought to inhibit inflammation and promote proper development of young, immature intestinal, respiratory and immune cells into healthy, fully mature cells.
For a Leaky gut, optimal digestion can be obtained through diet, therapeutic nutrition, and targeted supplementation to realize the complete resolution of symptoms. By changing what you eat and healing your gut you can clear your skin if leaky gut is the cause of your eczema
Final Thoughts
Leaky gut is associated with the disruption of the intestinal lining or tight junctions which controls the entrance of the particles from the digestive system into the bloodstream. Avoiding and including a certain type of foods with probiotic therapy helps in curing the disease.
The leaky gut syndrome is not a recognized diagnosis in the medical community yet. Eczema or Atopic dermatitis still remains a complex disease with mysteries in its actual cause and no complete treatment. Even in today’s advanced and latest medical improvements, there are still questions that remain unanswered. The connection between Leaky Gut and Atopic Dermatitis arises many thoughts with diagnostic and treatment implications but also raises many queries. Still, there are ongoing studies and more research required if Leaky gut is the key cause of eczema or just limited to certain sub-categories of Eczema and what will be the solution that needs to be approached.
GET IN CONTROL OF YOUR ECZEMA
Use our AI tool to check the severity of Eczema and keep track of your Eczema progress.