All you want to know about Anti-Inflammatory Diet for Eczema
Have you tried most of the moisturizers and topical creams for treating your eczema? And still, the symptoms are not in control? Then this blog is something you want to look forward to.
Now, we have a better understanding of what causes this chronic skin condition in the first place. That makes Eczema a complicated condition to treat and manage.
While eczema can be persistent, causing extreme discomfort, it doesn’t have to prevent eczema sufferers from living a happy life. It is always possible to improve the eczema symptoms by trying treatment methods and adapting your diet can play a critical role in doing so.
Our diet is an important medium to support and strengthen our skin. While eczema is a chronic skin condition that doesn’t have any quick fixes, our eating habits can have a positive impact on it.
Finding Food triggers
Identifying food triggers requires dedication and a lot of patience, but it’s worth it, to get that rash that itches under control. While Identifying the right diet is very crucial in eczema it is equally important to track the food that causes triggers. One of the verified ways of doing so is to try the elimination diet method. Wherein you need to maintain a diary and note down the foods you’ve eaten and how your body feels and look for patterns. Start by eliminating just one food for 3 weeks that you suspect. Similarly, Introduce one by done and note the changes.
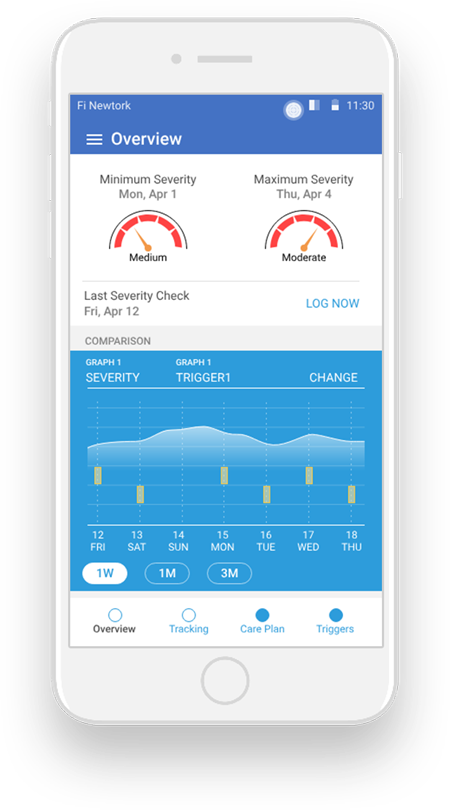
You can also log your food and track the food trigger just by clicking an image of the food using this eczema app.
The relation between Diet and Eczema
Eczema flares can be triggered by various factors in the environment. Frequent triggers include allergens, chemical irritants, high stress, sweating, obesity, dry skin, extreme temperatures, and dry climates (especially in the winter). Though with little evidence, food is one of them, many people start to feel their eczema symptoms worsens after consuming certain types of food. And Some people have even reported a reduction in their eczema symptoms by including certain foods into their diet.
The way that diet has its impact on eczema can be looked at in this perspective, eczema in a simple word is termed as skin inflammation or inflammatory skin disease. Hence, an Anti-inflammatory diet comes into consideration. Another factor which is something related to inflammatory response and closely associated with the itch, any guesses?? Histamine it is! Yes, the amount of histamine released and its tolerance in the body is something that is closely related to eczema symptoms. One of the best ways to know that your eczema symptoms are related to histamine is your Doctor will ask you to take an anti-histamine tablet when your condition is worse. If your condition improves that’s proof of a link. In such cases, a low histamine diet will really be helpful in controlling eczema exacerbation.
Hence, it is incredibly important to understand the difference between inflammatory and anti-inflammatory foods. Learning to eat more anti-inflammatory foods and eliminating inflammatory foods is key to managing eczema flare-ups when it comes to diet for eczema.
What is an Anti-Inflammatory diet?
The anti-inflammatory diet is an eating plan adapted to prevent or curb chronic inflammation in the body. Chronic Inflammation is a troublemaker, not only in eczema but a gamut of other health problems as well.
This Diet is completely based on whole plant foods. It includes vegetables, fresh fruits, legumes, intact whole grains, nuts, seeds, and non – processed foods. And the processed foods are thrown out of the picture or highly restricted.
The anti-inflammatory diet is all about filling your plate with foods that have been shown to fight inflammation and equally focusing on cutting out foods that have been shown to stimulate it.
Read more about foods to avoid in eczema as we have detailed with a list of top 10 common foods that exacerbate the eczema symptoms.
How an Anti-Inflammatory diet works
Inflammation is nothing but our body’s immune response to toxins and other foreign particles. As a natural part of metabolism, a lot of free radicals are released. In general, the inflammation subsides on its own. But in chronic cases, this inflammation remains for a longer period of time causing not only pain but also triggering chronic diseases, such as heart disease, diabetes, worsening eczema symptoms, etc
The antioxidants in anti-inflammatory diet work by reducing levels of free radicals which can lead to inflammation when they’re not held in check.
Similarly, if you are preparing to fight against histamine you want to consume more quercetin-rich foods. This compound is known to help stabilize mast cells to lower histamine levels and inflammation in addition to supporting gut health.
Anti-Inflammatory food that helps eczema
1) Vegetables



Vegetables are rich in flavonoids and carotenoids with both antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activity. Also, vitamin K in green leafy vegetables helps in reducing inflammation. It is advised to go for a rainbow that is to include vegetables of different colors at least 7 to 8 variety. You can eat them both raw and cooked, and choose organic whenever possible.
Choices
- Dark leafy greens (spinach, collard greens, kale, Swiss chard)
- Cruciferous vegetables (broccoli, cabbage, Brussels sprouts, kale, and cauliflower)
- Carrots
- Beets
- Onions
- Peas
- Squashes
- Raw and washed green salads
2) Fruits



Like vegetables fruits are also rich in carotenoids and flavonoids, moreover, the pigment that gives colors to the fruits helps in fighting inflammation. Again, try to include different colors of fruits to the diet and go for fresh seasonal fruits which are low in their glycemic load have as a whole fruit or chopped into pieces
Choices
- Berries (Raspberries, blueberries, strawberries, blackberries)
- Peaches
- Nectarines
- Oranges
- Pink grapefruit
- Red grapes
- Plums
- Pomegranates
- Cherries
- Apples
- Pears
3) Whole Grains



Whole grains are high in fiber which also helps in reducing inflammation. Moreover, they digest slowly, reducing the frequency of spikes in blood sugar that promote inflammation. Remember the grains that are intact or in a few large pieces fall under the whole grain category and not whole-wheat bread or other products made from flour.
Choices
- Oatmeal
- Brown rice
- Wild rice,
- Buckwheat groats,
- Barley,
- Quinoa,
- Steel-cut oats
4) Beans / Legumes



Beans are glycemic food power-packed with folic acid, magnesium, potassium, and soluble fiber. They are loaded with antioxidants and anti-inflammatory substances. A whole cooked can be added to your meal or the pureed form like hummus will elevate the taste of the dish.
Choices
- Chickpeas
- Black-eyed peas
- Anasazi,
- Adzuki
- Lentils
5) Herbs / Spices



Herbs and spices are known for their anti-oxidant and anti-inflammatory properties and are used to heal inflammation for ages. Generally, herbs and spices are used to season foods and add taste to it. Turmeric and ginger are powerful natural anti-inflammatory agents. Compounds such as curcumin found in turmeric is a strong antioxidant and powerful anti-inflammatory agent. Adding it to your daily meal will be beneficial
Choices
- Turmeric
- Ginger
- Garlic (dried and fresh)
- Chili peppers
- Basil
- Cinnamon
- Rosemary
- Thyme
6) Vitamins



You should maintain a proper balance of vitamins in their diet. Below Vitamins and minerals are particularly relevant for eczema:
Choices
- Vitamin C – found in brightly colored fruit, veg, and rosehip.
- Vitamin E – found in sunflower seeds, almonds, pine nuts, avocado, and dried apricots.
- Vitamin D – is absorbed from sunlight when it is sunny out there. You can also supplement vitamin D throughout the winter months.
- Vitamin K2 – Dark Green Leafy Vegetables
- Zinc – Dark Chocolate (Less sweet)
7) Probiotics



Probiotics are nothing but live microbes (usually bacteria) that can improve your health. They are good bacteria usually found in the lining of the digestive tract (gut). The understanding is that when you populate your gut with good bacteria through probiotic supplementation, you may be able to prevent or treat the symptoms of eczema.
Choices
- Fortified yogurt
- Soft cheeses (e.g. Gouda)
- Kefir
- Kombucha
- Miso soup
- Naturally fermented pickles
- Tempeh
- Unpasteurized sauerkraut
- Over the Counter Probiotic Supplement (After consulting)
8) Quercetin Rich Food
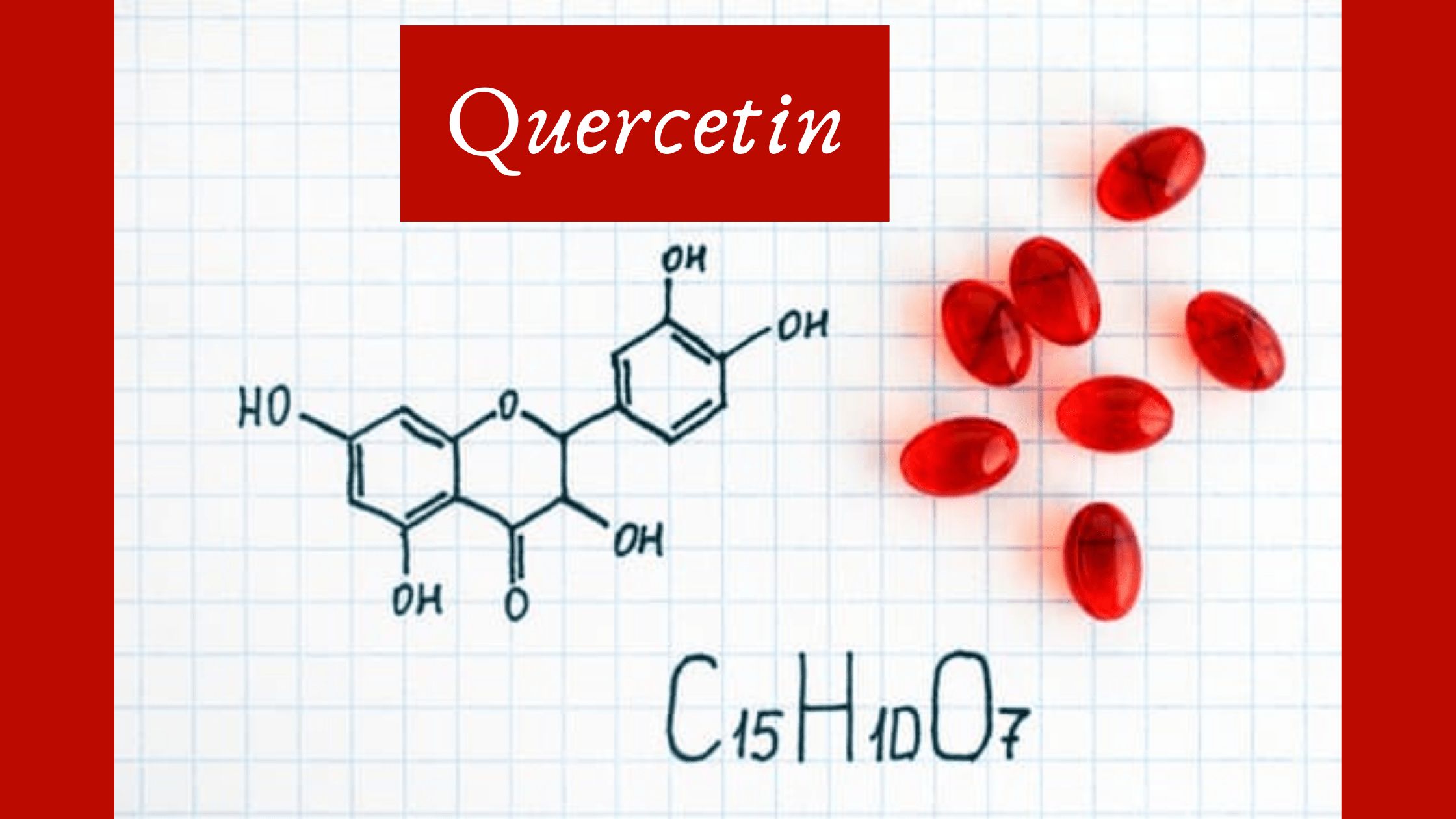


Quercetin is a flavonoid that is found in plants. Flavonoids have many health benefits but with regards to eczema, they work by reducing histamine release and boosting the skin’s ability to fight infection. That makes quercetin a powerful antioxidant with antihistamine properties that fight inflammation, helping to prevent eczema flare-ups.
Quercetin is found in onions, kale, broccoli, apples, tomatoes, green tea, and berries.
Choices
- Leafy vegetables
- Asparagus
- Tomatoes
- Red onions
- Apples
- Peppers
- Broccoli
- Black and green tea
- Berries
- Nectarines
9) Omega 3 Fatty Acid



Omega-3 fatty acids are required for skin health. They are known for their roles in reducing inflammation due to their strong anti-inflammatory property. Selected fishes are the number one source for omega-3 fats but if you do not eat fish you can go for distilled fish oil supplements or other plant sources mentioned below.
Choices
Non-veg source
- Salmon
- Tuna
- Herring
- Black cod
- Mackerel
- Sardines
- Anchovies
Veg source
- Flaxseed
- Walnuts
- Chia seeds
- Navy beans,
- Brussels sprouts
- Avocado
- Omega-3-fortified foods (including eggs and milk)
10) Healthy fats



Extra-virgin coconut oil, extra-virgin olive oil, walnuts, avocados, hemp seeds, flaxseed, flax oil. Healthy fats are those rich in either monounsaturated or omega-3 fats and thought to have the antioxidant activity absorbing the free radicals resulting in inflammation.
Choices
- Extra-virgin coconut oil
- Extra-virgin olive oil
- Walnuts
- Avocados, Avocado oil
- Hemp seeds
- Flaxseed, flax oil
- Hazelnut oils in salads
- Dark roasted sesame oil as a flavoring for soups and stir-fries
Tips on Following an Anti Inflammatory Diet For Eczema
- Eat five to nine servings of antioxidant-rich fruits and vegetables each day.
- Drink lots of water to replenish your body’s moisture.
- Identify Allergens from your Diet
- Eat Oily fish, nuts seeds 3 times a week.
- Limit your intake of foods high in omega-6 fatty acids such as vegetable oil, beef, pork and saturated fats
- Try seasoning your herbs and spices that act as an anti-inflammatory agent, instead of salt to add flavor.
- Go for the rainbow in fruits and vegetables i.e variety of bright color fruits and vegetables
- Take a vitamin D supplement daily, especially in winter months. · Go for healthier protein sources, such as lean poultry, fish, soy, beans, and lentils instead of red meat
- Swap out margarine and vegetable oils for the healthier fats found in olive oil, nuts, and seeds.
- Opt for fiber-rich whole grains like oats, quinoa, brown rice, bread, and pasta that list a whole grain as the first ingredient and avoid refined grains or flour.
- Maintenance of healthy body weight by routine exercise, if overweight or obese weight reduction will definitely help.
- Don’t let stress over tale you manage your stress by meditation techniques like yoga, mindfulness, etc.
Final Thoughts
Each Individual is different, so is the skin of each person, therefore the same food can act differently in two individuals. A food acting as the key anti-inflammatory agent reducing eczema symptoms in one person can be the inflammation striker in another person. It is always best to customize the diet for each person’s unique needs.
Remember any change takes its own time, being patient is the key while looking for impact through any program. It is well said that no battle is ever won or lost on a single meal, so consistency is the key to maintaining your Anti-inflammatory diet. What’s most important is the overall pattern of how you eat. Not only eating what’s right will help but you also pay equal focus on avoiding what’s wrong.
The anti-inflammatory diet is all about filling your meals with foods that have been shown the power to fight inflammation and equally focusing on cutting out foods that have been known to contribute to it.
Choose from a variety of, antioxidant-rich foods. It can help curb inflammation in combination with care routine like moisturizing, exercise, a good night’s sleep. Looking for your best combination of the above two may improve inflammation markers and possibly reduce your risk of developing eczema symptoms.
References
-Chung, Bo Young et al. “Treatment of Atopic Dermatitis with a Low-histamine Diet.” Annals of dermatology vol. 23 Suppl 1 ,Suppl 1 (2011): S91-5. doi:10.5021/ad.2011.23.S1.S91
-Fabisiak, Adam et al. “Targeting Histamine Receptors in Irritable Bowel Syndrome: A Critical Appraisal.” Journal of neurogastroenterology and motilityvol. 23,3 (2017): 341-348. doi:10.5056/jnm16203
-Ricker MA, Haas WC. Anti-Inflammatory Diet in Clinical Practice: A Review. Nutr Clin Pract. 2017;32(3):318-325. doi:10.1177/08845336177