Genital Psoriasis: Symptoms, Causes, and How to Treat It
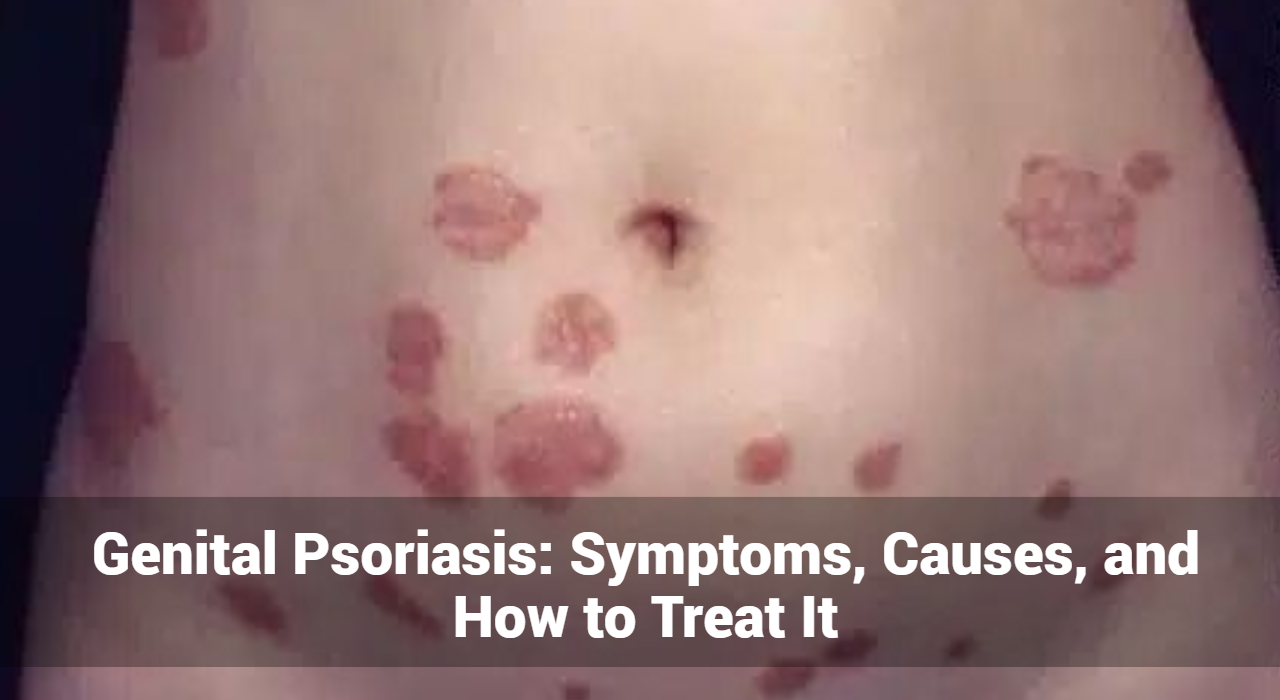
Genital psoriasis is a chronic skin condition that affects the genital area, causing discomfort and impacting the quality of life for those who suffer from it. This form of psoriasis, while less common than other types, requires careful management due to the sensitivity of the affected area. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the symptoms, causes, and treatment options for genital psoriasis, providing valuable insights for those affected by this condition.
What is Genital Psoriasis?
Genital psoriasis is a subtype of psoriasis that manifests in the skin around the genital area. Psoriasis is an autoimmune disorder characterized by the rapid turnover of skin cells, leading to the formation of red, scaly patches. When these patches occur in the genital region, they can cause significant discomfort and emotional distress.
What Are Common Symptoms of Genital Psoriasis?
Recognizing the symptoms of genital psoriasis is crucial for early diagnosis and treatment. The symptoms can vary depending on the specific area affected, but common signs include:
Red Patches
- Description: Smooth, shiny red patches are the hallmark of genital psoriasis.
- Location: These patches commonly appear on the vulva, penis, scrotum, inner thighs, buttocks, and around the anus.
Intense Itching and Burning
- Description: Severe itching and a burning sensation are frequent symptoms.
- Aggravating Factors: These symptoms can be exacerbated by sweat, heat, and friction from clothing or movement.
Pain and Discomfort
- Description: The affected areas can become painful, especially during physical activities.
- Impact: Walking, exercising, or engaging in sexual intercourse can increase pain and discomfort due to inflammation and swelling.
Minimal Scaling
- Description: Unlike psoriasis on other body parts, genital psoriasis typically lacks thick, silvery scales.
- Appearance: There may still be some degree of skin flaking or scaling, but it is usually less pronounced.
Fissures and Cracks
- Description: Severe cases of genital psoriasis can lead to cracks or fissures in the skin.
- Complications: These openings increase the likelihood of secondary infections and can be quite painful.
Erythema (Redness)
- Description: The skin in the genital area may appear red and inflamed.
- Spread: Redness can extend beyond the initial patches, affecting larger areas of the skin.
Varied Lesions
- Description: Lesions may vary in shape and size.
- Coalescence: Sometimes, smaller lesions merge to form larger affected areas, making the condition more extensive.
Localized Swelling
- Description: Swelling can occur around the affected areas, contributing to overall discomfort.
- Impact: Swelling can make hygiene more difficult and increase friction, leading to more irritation.
Maceration
- Description: Prolonged exposure to moisture can cause the skin to soften and break down.
- Risk: Macerated skin is more prone to infections and irritation, exacerbating symptoms.
Emotional and Psychological Impact
- Description: The symptoms of genital psoriasis can cause significant emotional distress.
- Impact: Patients may experience embarrassment, anxiety, depression, and social withdrawal due to the visible nature of the condition and its impact on intimate relationships.
Track and Manage your Eczema treatment using a comprehensive Eczema App
Download Eczemaless now
What Causes of Genital Psoriasis?
The exact cause of genital psoriasis, like other forms of psoriasis, is not fully understood. However, several factors are believed to contribute to its development:
Genetic Predisposition
- Description: A family history of psoriasis increases the likelihood of developing the condition.
- Genetic Factors: Specific genes have been identified that are associated with an increased risk of psoriasis.
Immune System Dysfunction
- Description: Psoriasis is an autoimmune disorder where the immune system mistakenly attacks healthy skin cells.
- Result: This causes rapid skin cell turnover, leading to the formation of plaques and inflammation.
Environmental Triggers
- Description: Various environmental factors can trigger or worsen psoriasis symptoms.
- Examples: Infections (bacterial or viral), cuts, scrapes, or other skin injuries can lead to the development of psoriasis plaques.
Hormonal Changes
- Description: Hormonal fluctuations can influence the severity of psoriasis.
- Periods: Changes during puberty, pregnancy, or menopause can trigger flare-ups or exacerbate existing symptoms.
Lifestyle Factors
- Description: Certain lifestyle choices can increase the risk of developing psoriasis or worsen symptoms.
- Examples: Smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, and obesity are all linked to a higher risk and severity of psoriasis.
Stress
- Description: Stress is a well-known trigger for psoriasis flare-ups.
- Management: Effective stress management techniques, such as yoga, meditation, and regular exercise, can help reduce the frequency and severity of flare-ups.
Diagnosis of Genital Psoriasis
Diagnosing genital psoriasis involves a combination of physical examination and medical history. A dermatologist will typically:
- Examine the Affected Area: A thorough examination of the genital area is conducted to assess the appearance of the skin lesions.
- Medical History: The doctor will ask about the patient’s medical history, including any family history of psoriasis or other autoimmune disorders.
- Skin Biopsy: In some cases, a skin biopsy may be performed to rule out other conditions that can mimic the symptoms of genital psoriasis, such as fungal infections or dermatitis.
GET IN CONTROL OF YOUR ECZEMA
Use our AI tool to check the severity of Eczema and keep track of your Eczema progress.
What are the treatment options for genital psoriasis?
Treating genital psoriasis requires a delicate approach due to the sensitivity of the area. Here are some effective treatment options:
Topical Treatments
- Corticosteroids: Low-potency corticosteroid creams or ointments are commonly prescribed to reduce inflammation and itching. Due to the thinness of the skin in the genital area, high-potency corticosteroids are generally avoided.
- Calcineurin Inhibitors: Tacrolimus and pimecrolimus are non-steroidal creams that can be used to reduce inflammation without the side effects associated with long-term corticosteroid use.
- Moisturizers: Regular use of moisturizers can help maintain skin hydration and reduce dryness and discomfort.
Systemic Treatments
- Oral Medications: In severe cases, oral medications such as methotrexate, cyclosporine, or acitretin may be prescribed to suppress the immune system and reduce inflammation.
- Biologic Therapies: Biologics are a newer class of medications that target specific components of the immune system. These are typically used for moderate to severe psoriasis and can be highly effective.
Lifestyle and Home Remedies
- Gentle Skincare: Using mild, fragrance-free soaps and avoiding hot water can prevent further irritation of the skin.
- Loose Clothing: Wearing loose-fitting clothing made of natural fibers can reduce friction and allow the skin to breathe.
- Stress Management: Stress is a known trigger for psoriasis flare-ups. Techniques such as yoga, meditation, and regular exercise can help manage stress levels.
Phototherapy
Phototherapy involves exposing the skin to controlled amounts of natural or artificial ultraviolet light. This treatment is usually performed in a medical setting under the supervision of consult a dermatologiest or healthcare professional.
Coping and Support
Living with genital psoriasis can be challenging, both physically and emotionally. Here are some tips for coping with the condition:
- Seek Support: Joining a support group or seeking counseling can provide emotional support and practical advice from others who understand what you are going through.
- Educate Yourself: Learning more about genital psoriasis and its management can empower you to take control of your condition.
- Communicate with Your Partner: Open communication with your partner about your condition can help maintain intimacy and reduce anxiety related to sexual activity.
Conclusion
Genital psoriasis is a complex condition that requires careful management and a comprehensive treatment plan. By understanding the symptoms, causes, and treatment options, individuals affected by genital psoriasis can take proactive steps to manage their condition and improve their quality of life. If you suspect you have genital psoriasis, it is essential to consult a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and personalized treatment plan. With the right approach, it is possible to effectively manage genital psoriasis and minimize its impact on your daily life.
Track and Manage your Eczema treatment using a comprehensive Eczema App
Download Eczemaless now